Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Animals
AnimalsThis lizard can tolerate extreme levels of lead
Cuban brown anoles have the highest blood lead levels of any vertebrate known — three times that of the previous record holder, the Nile crocodile.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Life
LifeHorses may have become rideable with the help of a genetic mutation
To make horses rideable during domestication, people may have inadvertently targeted a mutation in horses to strengthen their backs and their balance.
By Jake Buehler -
 Microbes
MicrobesWhat makes chocolate taste so good? It’s the microbes
Beans matter, but microbes may be the real secret to fine chocolate flavor. Scientists are building starter cultures that may improve quality.
-
 Animals
AnimalsThe mysterious, extinct ‘Fuegian dog’ was actually a semi-tame fox
Historic European accounts long described the canids as domesticated dogs. A new study suggests that’s probably not true.
By Jake Buehler -
 Animals
AnimalsThe phoenix isn’t the only critter to survive the flames
There are no real phoenixes hiding anywhere. But science has revealed that some living things can take quite a bit of heat.
-
 Animals
AnimalsAround the world, birds sing longer in light-polluted areas
In light-polluted landscapes, birds' singing time is an average of 50 minutes longer per day. It's still unclear if this hurts bird health or helps.
By Jake Buehler -
 Animals
AnimalsFrilly bug feet inspire a water-striding robot
Ripple bugs’ nimble movements on the surface of water inspired a robot with automatically unfurling fans on its feet.
-
 Animals
AnimalsThese giant carnivorous bats hug, cuddle — and even share dinner
Infrared cameras in Costa Rica revealed that the world’s largest carnivorous bat maintains close social bonds through wing wraps and prey sharing.
By Jay Kakade -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineCould babies get bird flu through breast milk? Maybe, a study hints
H5N1 bird flu might infect human mammary glands, potentially allowing the virus to show up in breast milk.
-
 Animals
AnimalsStreaked shearwaters poop only while flying over the ocean
In-flight defecation may help the birds stay away from feces that can contain pathogens such as bird flu while also fertilizing the ocean.
-
 Animals
AnimalsA single protein makes lovesick flies spill their guts
Producing a male-specific protein in digestion-related neurons may have led to the evolution of an odd “romantic” barfing behavior in one species of fruit flies.
-
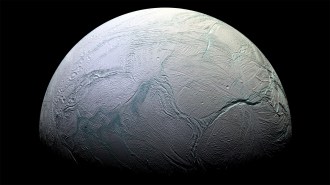 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceCosmic rays could, in theory, sustain life on other worlds
The hypothesis could extend the search for extraterrestrial life to include frigid planets with thin atmospheres and underground water.