Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Health & Medicine
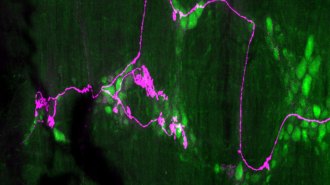
Health & MedicineFull intestines, more than full stomachs, may tell mice to stop eating
A new description of stretch-sensing nerve endings in mice’s intestines could lead to ways to treat obesity.
-
 Animals
AnimalsHumpback whales in the South Atlantic have recovered from near-extinction
A new count shows the population off Brazil went from about 450 in the 1950s to some 25,000 today.
-
 Climate
Climate5 things to know about fighting climate change by planting trees
One group’s idea of planting vast swaths of trees to curb climate change exaggerates the proposal’s power to trap carbon, some argue.
By Susan Milius -
 Animals
AnimalsA tooth fossil shows Gigantopithecus’ close ties to modern orangutans
Proteins from the past help clarify how an ancient Asian ape that was larger than a full-grown, modern male gorilla evolved.
By Bruce Bower -
 Earth
EarthPlastics outnumber baby fish 7-to-1 in some coastal nurseries
Ocean slicks serve as calm, food-rich nurseries for larval fish. A new study shows that slicks also accumulate plastics, which get eaten by baby fish.
-
 Animals
AnimalsFlipping a molecular switch can turn warrior ants into foragers
Toggling one protein soon after hatching makes Florida carpenter ants turn from fighting to hunting for food.
By Jake Buehler -
 Animals
AnimalsPower lines may mess with honeybees’ behavior and ability to learn
Under power lines, honeybees might suffer neurological effects from exposure to electromagnetic fields.
-
 Animals
AnimalsSilver-backed chevrotains have been ‘rediscovered’ by science after 29 years
With help from Vietnamese villagers, researchers captured photos of a species of deerlike ungulate thought lost to science nearly three decades ago.
-
 Life
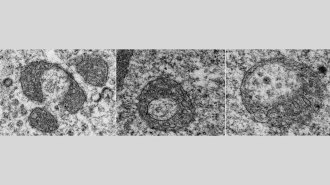
LifeSelf-destructing mitochondria may leave some brain cells vulnerable to ALS
Mitochondria that appear to dismantle themselves in certain brain cells may be a first step toward ALS, a mouse study suggests.
-
 Neuroscience
NeurosciencePeople who lack olfactory bulbs shouldn’t be able to smell. But some women can
Some women who appear to lack the brain structures that relay scent messages still have an average sense of smell, and scientists have no idea how.
By Sofie Bates -
 Ecosystems
EcosystemsCan forensics help keep endangered rosewood off the black market?
Timber traffickers are plundering the world’s forests, but conservationists have a new set of tools to fight deforestation.
By Edward Carver and Sandy Ong -
 Animals
AnimalsApple TV+’s ‘The Elephant Queen’ shies away from hard truths
The Elephant Queen offers an intimate look into the lives of elephants, but the documentary largely avoids threats the animals face.