Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Animals
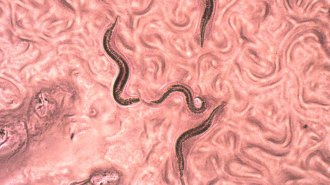
AnimalsDevil worm genes hold clues for how some animals survive extreme heat
Devil worms have many extra copies of genes tied to heat stress and cell death, which may help the critters survive deep underground, a study finds.
By Sofie Bates -
 Life
LifeA tree in Brazil’s arid northeast rains nectar from its flowers
Northeast Brazil is home to a tree that entices bat pollinators by making a “sweet rain” of nectar.
By Jake Buehler -
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceIs taking birth control as a teen linked to depression? It’s complicated
As researchers sift through conflicting data, no clear answers emerge on whether birth control during teenage years can cause depression later.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineA dose of ketamine could lessen the lure of alcohol
Ketamine may weaken wobbly memories of drinking, a trick that might ultimately be useful for treating alcohol addiction.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineA protein helps disease-causing immune cells invade MS patients’ brains
Blocking the protein may hinder B cells invading the brain in multiple sclerosis, a study in mice and ‘stand-in’ human brain barriers finds.
By Sofie Bates -
 Humans
HumansWhy screening DNA for ‘designer babies’ probably won’t work
While simulations suggest it’s possible to predict a child’s height from looking at an embryo’s DNA, real-world examples say otherwise.
-
 Neuroscience
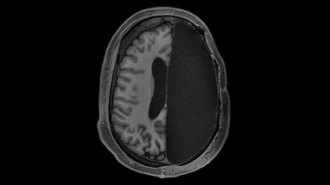
NeuroscienceSome people with half a brain have extra strong neural connections
Brain scans of six people who had half their brains removed as epileptic children show signs of compensation.
-
 Life
LifeCaribou migrate farther than any other known land animal
Caribou in Alaska and Canada migrate up to 1,350 kilometers round trip each year, a study reports.
By Sofie Bates -
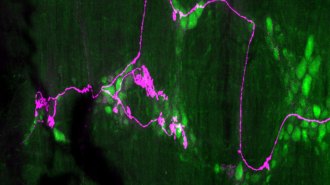 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineFull intestines, more than full stomachs, may tell mice to stop eating
A new description of stretch-sensing nerve endings in mice’s intestines could lead to ways to treat obesity.
-
 Animals
AnimalsHumpback whales in the South Atlantic have recovered from near-extinction
A new count shows the population off Brazil went from about 450 in the 1950s to some 25,000 today.
-
 Climate
Climate5 things to know about fighting climate change by planting trees
One group’s idea of planting vast swaths of trees to curb climate change exaggerates the proposal’s power to trap carbon, some argue.
By Susan Milius -
 Animals
AnimalsA tooth fossil shows Gigantopithecus’ close ties to modern orangutans
Proteins from the past help clarify how an ancient Asian ape that was larger than a full-grown, modern male gorilla evolved.
By Bruce Bower