Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Paleontology
PaleontologyScience News’ favorite fossils of 2019
Fossil discoveries reported this year included Cambrian creatures, ancient bone cancer and a peek at life’s recovery after the dinosaur die-off.
-
 Microbes
MicrobesAirplane sewage may be helping antibiotic-resistant microbes spread
Along with drug-resistant E. coli, airplane sewage contains a diverse set of genes that let bacteria evade antibiotics.
-
 Life
LifeOcean acidification could degrade sharks’ tough skin
Nine weeks of exposure to acidic seawater corroded the toothlike denticles that make up a puffadder shyshark’s skin, a small experiment found.
-
 Life
LifeKoalas aren’t primates, but they move like monkeys in trees
With double thumbs and a monkey-sized body, an iconic marsupial climbs like a primate.
By Susan Milius -
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyDNA from 5,700-year-old ‘gum’ shows what one ancient woman may have looked like
From chewed birch pitch, scientists recovered DNA from an ancient woman and her mouth microbes and hazelnut and duck DNA from a meal she’d consumed.
By Sofie Bates -
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceMice watching film noir show the surprising complexity of vision cells
Only about 10 percent of mice’s vision cells behaved as researchers expected they would, a study finds.
-
 Animals
AnimalsA year of big numbers startled the world into talking about nature
One million species are at risk. Three billion birds have been lost. Plus surges in Amazon burning.
By Susan Milius -
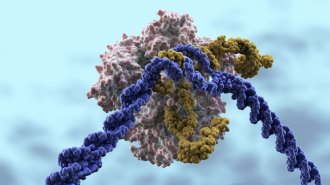 Genetics
GeneticsThe first U.S. trials in people put CRISPR to the test in 2019
Trials of the gene editor in people began in the United States this year, a first step toward fulfilling the technology’s medical promise.
-
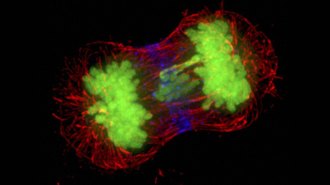 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineSurplus chromosomes may fuel tumor growth in some cancers
Extra copies of some genes on excess chromosomes may keep cancer cells growing. Without those extras, cancer cells form fewer tumors in mice.
-
 Animals
AnimalsTexas has its own rodeo ant queens
New species of rodeo ants, riding on the backs of bigger ants, turned up in Austin, Texas.
By Susan Milius -
 Animals
AnimalsA biochemist’s extraction of data from honey honors her beekeeper father
Tests of proteins in honey could one day be used to figure out what bees are pollinating and which pathogens they carry.
-
 Animals
AnimalsWhy some whales are giants and others are just big
Being big helps whales access more food. But how big a whale can get is influenced by whether it hunts for individual prey or filter-feeds.