Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Paleontology
PaleontologyA squid fossil offers a rare record of pterosaur feeding behavior
150 million years ago, a pterosaur attempted to snatch a squid from the ocean surface and lost a tooth in the process.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHow one woman became the exception to her family’s Alzheimer’s history
A single mutation in a woman who evaded Alzheimer’s may point to new ways to treat the disease.
-
 Life
LifeSparkly exoskeletons may help camouflage beetles from predators
Iridescence, normally thought to help insects stand out, can also camouflage beetles from predators, according to new experimental evidence.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsAncient kids’ DNA reveals new insights into how Africa was populated
Four long-dead youngsters from west-central Africa have opened a window on humankind’s far-flung African origins.
By Bruce Bower -
 Animals
AnimalsCollectors find plenty of bees but far fewer species than in the 1950s
An analysis of global insect collections points to a major collapse in bee diversity since the 1990s.
By Yao-Hua Law -
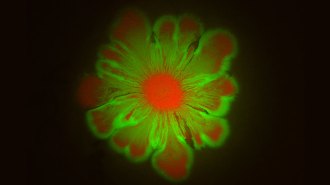 Life
LifeHow bacteria create flower art
Different types of microbes growing in lab dishes can push each other to make floral patterns.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHairy cells in the nose called brush cells may be involved in causing allergies
Some hairy cells in the nose may trigger sneezing and allergies to dust mites, mold and other substances, new work with mice suggests.
-
 Animals
AnimalsA naturalist writes an homage to bird migration
In ‘A Season on the Wind,’ Kenn Kaufman shares his lifelong obsession for and awe of spring bird migration.
By Diana Steele -
 Life
Life‘PigeonBot’ is the first robot that can bend its wings like a real bird
Insights into the joint movements and feather surface structures that help birds control their wing shape could help robotic flyers move more deftly.
-
 Life
LifeThe ‘Blob,’ a massive marine heat wave, led to an unprecedented seabird die-off
Scientists have linked thousands of dead common murres in 2015–2016 to food web changes caused by a long-lasting marine heat wave nicknamed the Blob.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceA parasite that makes mice unafraid of cats may quash other fears too
The parasite Toxoplasma gondii can mess with all sorts of mice behaviors and make the rodents fearless in many situations.
-
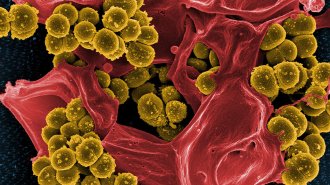 Microbes
MicrobesMicrobes slowed by one drug can rapidly develop resistance to another
Hunkering down in a dormant, tolerant state may make it easier for infectious bacteria to develop resistance to antibiotics.