Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Life
LifeThis is the first deep-sea fish known to be a mouthbreeder
Scientists found over 500 eggs attached to the inside of a parazen fish’s mouth.
By Jake Buehler -
 Animals
AnimalsSea turtles may confuse the smell of ocean plastic with food
Sea turtles respond to the smell of plastic that’s been in the ocean similarly to food, suggesting the reptiles may end up eating the harmful debris.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceBrain waves common during sleep also show up in awake sheep
Sleep spindles, thought to help solidify memories in people, may do similar work during wakefulness if these daytime ripples occur in humans.
-
 Animals
AnimalsBright yellow spots help some orb weaver spiders lure their next meal
Experiments with cardboard arachnids suggest that orb weaver spiders have evolved yellow colorations on their undersides to attract bees and moths.
By Yao-Hua Law -
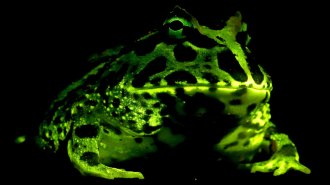 Animals
AnimalsGlowing frogs and salamanders may be surprisingly common
A widespread ability to glow in striking greens, yellows and oranges could make amphibians easier to track down in the wild.
-
 Life
LifeA distant cousin of jellyfish may survive without working mitochondria
A tiny creature that parasitizes salmon is the first known multicellular eukaryote without a mitochondrial genome, a hallmark of complex life.
-
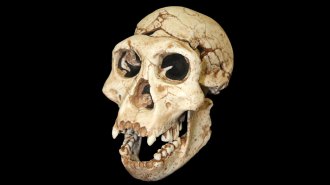 Humans
HumansThe earliest known hominid interbreeding occurred 700,000 years ago
The migration of Neandertal-Denisovan ancestors to Eurasia some 700,000 years ago heralded hookups with a resident hominid population.
By Bruce Bower -
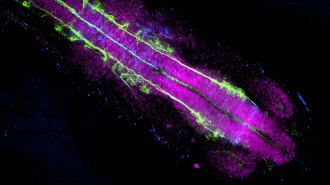 Life
LifeHow African turquoise killifish press the pause button on aging
The fish’s embryos can enter a state of suspended growth to survive dry spells. A study shows that state protects them from aging, and hints at how.
-
 Life
LifeA new lizard parasite is the first known to move from mom to baby
Nematodes were found living in a lizard’s ovaries and the braincase of her embryos — the first evidence of a reptile parasite that jumps generations.
By Pratik Pawar -
 Animals
AnimalsOne blind, aquatic salamander may have sat mostly still for seven years
Olms may live for about century and appear to spend their time moving sparingly.
By Jake Buehler -
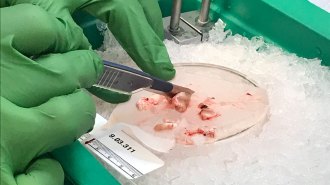 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceLiving brain tissue experiments raise new kinds of ethical questions
An ethicist describes the quandaries raised by working with tissue involved in human awareness.
-
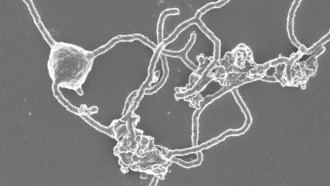 Life
LifeMicrobiologists took 12 years to grow a microbe tied to complex life’s origins
Years of lab work resulted in growing a type of archaea that might help scientists understand one of evolution’s giant leaps toward complexity.