Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Animals
AnimalsCold War nuclear test residue offers a clue to whale sharks’ ages
One unexpected legacy of the Cold War: Chemical traces of atomic bomb tests are helping scientists figure out whale shark ages.
-
 Animals
AnimalsSeabirds may find food at sea by flying in a massive, kilometers-wide arc
Radar shows that seabird groups can fly together in giant “rake” formations. If they are cooperating to find food, it’s on a scale not yet seen in the birds.
By Jake Buehler -
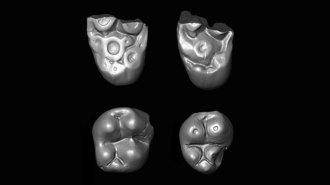 Paleontology
PaleontologyTwo primate lineages crossed the Atlantic millions of years ago
Peruvian primate fossils point to a second ocean crossing by a now-extinct group roughly 35 million to 32 million years ago.
By Bruce Bower -
 Animals
AnimalsHitchhiking oxpeckers warn endangered rhinos when people are nearby
Red-billed oxpeckers do more than just eat parasites from rhinos’ backs. The birds can alert the hunted mammals to potential danger, a study finds.
-
 Environment
EnvironmentA year long expedition spotlights night life in the Arctic winter
Scientists anchored to an ice floe near the North Pole are investigating how life survives polar night and what changes will occur as the Arctic continues to warm.
By Shannon Hall -
 Life
LifeThe Great Barrier Reef is suffering its most widespread bleaching ever recorded
Major bleaching events are recurring with increasing frequency on the Great Barrier Reef, hindering its recovery.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsThe PBS documentary ‘The Gene’ showcases genetics’ promise and pitfalls
A film from executive producer Ken Burns delivers an unfiltered history of genetics, showing how the science has helped and hurt people.
-
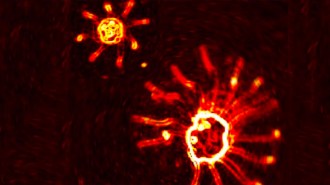 Life
LifeAlgae use flagella to trot, gallop and move with gaits all their own
Single-celled microalgae, with no brains, can coordinate their “limbs” into a trot or fancier gait.
By Susan Milius -
 Chemistry
ChemistryBeets bleed red but a chemistry tweak can create a blue hue
A new blue dye derived from beet juice might prove an alternative to synthetic blue dyes in foods, cosmetics or fabrics.
By Carmen Drahl -
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceMice’s facial expressions can reveal a wide range of emotions
Pleasure, pain, fear and other feelings can be reflected in mice’s faces, sophisticated computational analyses show.
-
 Animals
AnimalsA cat appears to have caught the coronavirus, but it’s complicated
While a cat in Belgium seems to be the first feline infected with SARS-CoV-2, it’s still unclear how susceptible pets are to the disease.
-
 Animals
AnimalsParasitic worm populations are skyrocketing in some fish species used in sushi
Fishes worldwide harbor 283 times the number of Anisakis worms as fishes in the 1970s. Whether that’s a sign of environmental decline or recovery is unclear.
By Amber Dance