Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Animals
AnimalsHow frigid lizards falling from trees revealed the reptiles’ growing cold tolerance
Some Florida lizards’ ability to handle temperatures down to 5.5° C may provide clues to how they might deal with the extremes of climate change.
-
 Anthropology
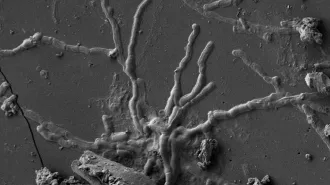
AnthropologyThese human nerve cell tendrils turned to glass nearly 2,000 years ago
Part of a young man’s brain was preserved in A.D. 79 by hot ash from Mount Vesuvius’ eruption.
-
 Life
LifeOgre-faced spiders catch insects out of the air using sound instead of sight
A new study finds that ogre-faced spiders can hear a surprisingly wide range of sounds.
-
 Animals
AnimalsHow octopuses ‘taste’ things by touching
Octopus arms are dotted with cells that can "taste" by touch, which might enable arms to explore the seafloor without input from the brain.
-
 Microbes
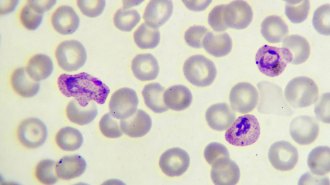
MicrobesHow malaria parasites hide from the human immune system
By turning genes on or off, the parasite keeps blood levels low but persistent, so infection doesn’t set off alarm bells for the immune system.
-
 Humans
HumansThe longest trail of fossilized human footprints hints at a risky Ice Age trek
Researchers have discovered the world's longest trail of fossilized human footprints at White Sands National Park, New Mexico.
-
 Animals
AnimalsWhy bat scientists are socially distancing from their subjects
Scientists are calling for a “hands-off” approach to research to decrease the chances of spreading the coronavirus to bats in North America.
-
 Paleontology
PaleontologyBat-winged dinosaurs were clumsy fliers
The two known species of bat-winged dinosaurs were a dead end when it comes to the evolution of bird flight, a new study finds.
-
 Animals
AnimalsThe diabolical ironclad beetle can survive getting run over by a car. Here’s how
The diabolical ironclad beetle is an incredibly tough little creature. A peek inside its exoskeleton reveals what makes it virtually uncrushable.
-
 Animals
AnimalsNaked mole-rats invade neighboring colonies and steal babies
Naked mole-rats invade neighboring colonies, steal pups and evict any others left behind. The show of force may be central to their underground lifestyle.
By Jake Buehler -
 Animals
AnimalsFire ants build little syphons out of sand to feed without drowning
To escape a watery death, some fire ants use build sand structures that draw the insects’ sugary, liquid food out of containers and to a safer place.
-
 Animals
AnimalsA rope bridge restored a highway through the trees for endangered gibbons
When critically endangered Hainan gibbons started making dangerous leaps across a new gully, researchers came up with an alternative route.