Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Life
LifeThese are the 5 costliest invasive species, causing billions in damages
Invasive species have cost the global economy at least $1 trillion since 1970 and $162.7 billion in 2017 alone. The annual cost is increasing.
-
 Animals
AnimalsWeather radar shows 30 metric tons of grasshoppers swarmed Las Vegas one night
Everything’s glitzier in Las Vegas. The most intensely lit U.S. city shows the impact of artificial light on insects on a megascale.
By Susan Milius -
 Animals
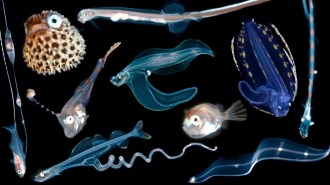
AnimalsDazzling underwater photos capture new views and scientific detail of fish larvae
Lab specimens of fish larvae are often mangled and bleached. Divers and researchers have partnered to study their rich colors and intricate bodies.
-
 Ecosystems
EcosystemsHow kelp forests off California are responding to an urchin takeover
A pair of studies reports 95 percent loss of kelp forests along the northern coast while sea otters are helping maintain surviving kelp farther south.
-
 Animals
AnimalsA toxin behind mysterious eagle die-offs may have finally been found
A 20-year study of water weeds and cyanobacteria in the southern United States pinpoints a bird-killing toxin, and it's not your usual suspect.
By Susan Milius -
 Ecosystems
EcosystemsSimple hand-built structures can help streams survive wildfires and drought
Building simple structures with sticks and stones — and inviting in dam-building beavers — can keep water where it’s needed to fight drought and wildfires.
-
 Animals
AnimalsA gene defect may make rabbits do handstands instead of hop
Mutations in a gene typically found throughout the nervous system rob rabbits of their ability to hop. Instead, the animals walk on their front paws.
-
 Life
LifeA plant gene may have helped whiteflies become a major pest
An agricultural pest may owe part of its success to a plant detox gene it acquired long ago that lets the insect neutralize common defenses.
-
 Animals
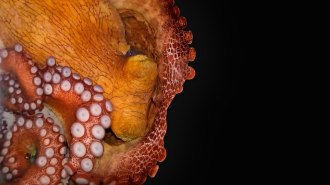
AnimalsOctopus sleep includes a frenzied, colorful, ‘active’ stage
Four wild cephalopods snoozing in a lab had long stretches of quiet napping followed by brief bursts of REM-like sleep.
-
 Animals
AnimalsDim lighting may raise the risk of a West Nile virus exposure
Dimly lit nights increased risk of West Nile virus exposure in chickens. Artificial light proved a better predictor of risk than population or paving.
-
 Animals
AnimalsWhy do sea turtles, penguins and sharks sometimes just swim in circles or spirals?
Tracking devices recorded the loops and spirals of 10 marine species. In some cases, scientists have good guesses for why; other times it’s baffling.
By Susan Milius -
 Genetics
Genetics‘The Code Breaker’ tells the story of CRISPR pioneer Jennifer Doudna
In his latest book, Walter Isaacson chronicles the discovery of CRISPR and delves into the ethics of gene editing.