Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Animals
AnimalsThe teeth of ‘wandering meatloaf’ contain a rare mineral found only in rocks
The hard, magnetic teeth of the world’s largest chiton contain nanoparticles of santabarbaraite, a mineral never seen before in biology.
-
 Chemistry
ChemistryA sweet father-son bond inspires tasty new molecule models
New edible models of proteins could spark students’ interest in the world of chemistry, especially students who are blind.
By Carmen Drahl -
 Neuroscience
NeurosciencePlaying brain training games regularly doesn’t boost brainpower
Comparing brain training program users with those who don’t do the mini brain workouts, scientists found no proof that the regimens boosted brainpower.
-
 Animals
AnimalsGray wolves scare deer from roads, reducing dangerous collisions
The predators use roads as travel corridors, creating “a landscape of fear” that keeps deer away and saves millions of dollars a year, a study finds.
By Jack J. Lee -
 Genetics
GeneticsA gene-based therapy partially restored a blind man’s vision
Light-activated proteins inserted in eye nerve cells and special goggles help the man, who lost his sight due to retinitis pigmentosa, see objects.
-
 Animals
AnimalsUrchin mobs team up to butcher sea stars that prey on them
Urchins are important herbivores in nearshore ecosystems, but are not strict vegetarians, with hunger that extends even to munching predatory nemeses.
By Jake Buehler -
 Climate
Climate‘Tree farts’ contribute about a fifth of greenhouse gases from ghost forests
Greenhouse gases from dead trees play an important role in the overall environmental impact of ghost forests, a new study suggests.
-
 Animals
AnimalsMammal brains may use the same circuits to control tongues and limbs
When mice drink water, they make corrective motions with their tongues that resemble similar adjustments made by primates when they grab for objects.
-
 Life
LifeEuropean fire ant chemicals may send spiders scurrying away
Black widows and some other common spider species avoid spaces where fire ants once roamed, suggesting the insects could inspire a spider repellent.
-
 Animals
AnimalsThe U.S.’s first open-air genetically modified mosquitoes have taken flight
After a decade of argument, Oxitec pits genetically modified mosquitoes against Florida’s spreaders of dengue and Zika.
By Susan Milius -
 Animals
AnimalsElephants are dying in droves in Botswana. Scientists don’t know why
Some type of pathogen may be behind the recent deaths of 39 elephants, a new wave that follows 350 deaths last summer.
-
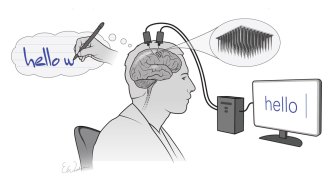 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceBrain implants turn imagined handwriting into text on a screen
A person who was paralyzed from the neck down was able to communicate, thanks to brain-to-text technology.