Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Life
Life‘Wild Souls’ explores what we owe animals in a human-dominated world
The new book Wild Souls explores the ethical dilemmas of saving Earth’s endangered animals.
-
 Paleontology
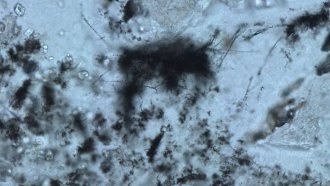
Paleontology3.42-billion-year-old fossil threads may be the oldest known archaea microbes
The structure and chemistry of these ancient cell-like fossils may hint where Earth’s early inhabitants evolved and how they got their energy.
-
 Paleontology
PaleontologyPterosaurs may have been able to fly as soon as they hatched
A fossil analysis shows the flying reptile hatchlings had a stronger bone crucial for lift-off that adults and shorter, broader wings for agility.
-
 Animals
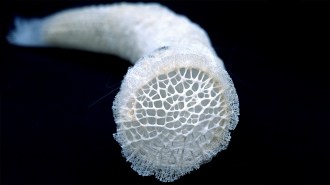
AnimalsHow intricate Venus’s-flower-baskets manipulate the flow of seawater
Simulations show that a deep-sea glass sponge’s intricate skeleton creates particle-trapping vortices and reduces the stress of rushing water.
By Nikk Ogasa -
 Animals
AnimalsThis butterfly is the first U.S. insect known to go extinct because of people
A 93-year-old Xerces blue specimen’s DNA shows that the butterfly is a distinct species, making it the first U.S. insect humans drove to extinction.
By Jake Buehler -
 Microbes
MicrobesMissing Antarctic microbes raise thorny questions about the search for aliens
Scientists couldn’t find microbial life in soils from Antarctica, hinting at a limit for habitability on Earth and other worlds.
By Elise Cutts -
 Life
LifePikas survive winter using a slower metabolism and, at times, yak poop
Pikas endure bone-chilling temperatures on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau by reducing their metabolism, and when possible, eating yak poop.
-
 Animals
AnimalsClimate change may be leading to overcounts of endangered bonobos
A changing climate in Congo is affecting how scientists count bonobos’ nests, possibly skewing estimates of the great ape population, a study suggests.
By Pratik Pawar -
 Humans
HumansOnly a tiny fraction of our DNA is uniquely human
Some of the exclusively human tweaks to DNA may have played a role in brain evolution.
-
 Paleontology
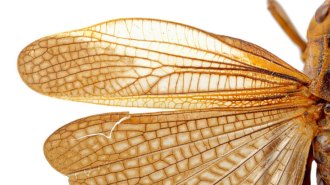
PaleontologyInsects had flashy, noise-making wings as early as 310 million years ago
The structure of a grasshopper-like insect’s fossilized wing suggests it crackled and reflected light, perhaps to attract mates or warn off predators.
-
 Animals
AnimalsWould dogs return the favor if you gave them treats? It’s complicated
An experiment in which dogs did not reciprocate food giving with humans may reveal something about the dogs, or about how science is done.
By Betsy Mason -
 Animals
AnimalsClimate change may rob male dragonfly wings of their dark spots
Less colorful, cooler wings may be advantageous to dragonflies in a warmer world. But the change could mess with the insects’ mating.
By Jake Buehler