
Neuroscience
Yaks may hint at a way to treat brain diseases like MS
A genetic mutation tied to keeping the brain healthy at high altitudes may point to a way to repair nerve damage, experiments in mice show.
By Simon Makin
Every print subscription comes with full digital access

A genetic mutation tied to keeping the brain healthy at high altitudes may point to a way to repair nerve damage, experiments in mice show.
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
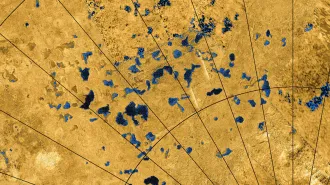
An experiment mimicking conditions on the Saturn moon suggests that cell-like bubbles don’t form in methane lakes, puncturing hopes for alien life.

The Amazon molly reproduces without sex. A genomic copy-and-paste trick called gene conversion may explain how it avoids evolutionary meltdown.

Submerged bees breathe and use strategies that don’t require oxygen, lab tests show. In nature, that trick could help the bees survive floods.

Ultraviolet cameras captured faint electrical flashes from leaves and branches as storm charges built up in the atmosphere.

A new study reports signs that nerve cells in the brain keep dividing over the decades. It’s not so simple.

As koalas in southern Australia have grown from a few hundred to almost half a million, the marsupials show signs of regaining lost genetic variation.

Chickpeas produced seeds in simulated lunar soil, offering clues for future space farming.

The wood-feeding cockroach’s cannibalistic love bites lead to a lasting bond. Afterward, the pair prefer each other over all other roaches.

Lucid dreamers who heard puzzle-linked soundtracks while sleeping were more likely to solve those unsolved problems the next day.
Subscribers, enter your e-mail address for full access to the Science News archives and digital editions.
Not a subscriber?
Become one now.