Humans
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Health & Medicine
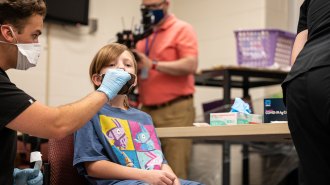
Health & MedicineCOVID-19 testing in schools works. So why aren’t more doing it?
School COVID-19 testing programs can keep kids in class and safe, but face challenges ranging from deciding on a testing strategy to parental buy-in.
-
 Psychology
PsychologyNostalgia may have bona fide benefits in hard times, like the pandemic
Once described as a disease, nostalgia’s reputation is much improved. Researchers hope to develop mental health therapies that trigger these memories.
By Sujata Gupta -
 Archaeology
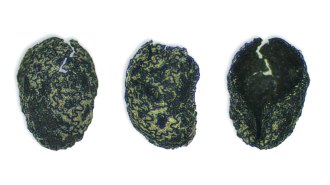
ArchaeologyThe earliest evidence of tobacco use dates to over 12,000 years ago
Burned seeds at an archaeological site in Utah hint at tobacco’s popularity long before it was domesticated.
By Bruce Bower -
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyDog DNA reveals ancient trade network connecting the Arctic to the outside world
People in Siberia were exchanging canines and probably other goods as early as 7,000 years ago with cultures as far off as Europe and the Near East.
By Freda Kreier -
 Anthropology
AnthropologyHow catching birds bare-handed may hint at Neandertals’ hunting tactics
By pretending to be Neandertals, researchers show that the ancient hominids likely had the skills to easily hunt crowlike birds called choughs.
-
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyHow our SN 10 scientists have responded to tumultuous times
COVID-19, social justice movements and the realities of climate change have given our Scientists to Watch new perspective.
-
 Chemistry
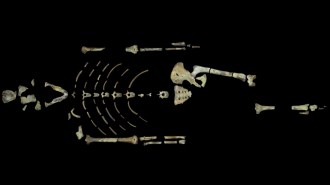
ChemistryRadiometric dating puts pieces of the past in context. Here’s how
Carbon dating and other techniques answer essential questions about human history, our planet and the solar system.
By Sid Perkins -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineA custom brain implant lifted a woman’s severe depression
An experimental device interrupts brain activity linked to a woman’s low mood. The technology, she said, has changed her lens on life.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineDiscovering how we sense temperature and touch wins the 2021 medicine Nobel Prize
Finding sensors on nerve cells that detect temperature and pressure nets California scientists David Julius and Ardem Patapoutian a Nobel Prize.
By Tina Hesman Saey and Freda Kreier -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineA new antiviral pill cuts COVID-19 hospitalization and death rates
Merck says its drug, molnupiravir, stops viral replication and can be taken right after a COVID-19 diagnosis.
-
 Anthropology
Anthropology50 years ago, X-rays revealed what ancient Egyptians kept under wraps
In the 1970s, scientists used X-rays to unravel mummy secrets. Now, advances in technology are providing unprecedented views of ancient Egyptians.
By Bruce Bower -
 Neuroscience
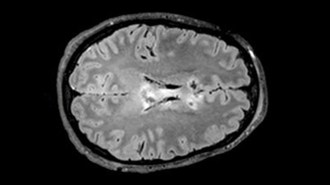
NeuroscienceA blood test may help predict recovery from traumatic brain injury
High levels of a key blood protein point to brain shrinkage and damage to message-sending axons, providing a biomarker for TBI severity and prognosis.