Humans
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Climate
ClimateVikings may have fled Greenland to escape rising seas
Vikings abandoned Greenland in the 15th century. Lower temperatures, an expanding ice sheet and rising sea levels may have played a role in their departure.
By Freda Kreier -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineCOVID-19 testing is complicated right now. Here are answers to 6 big questions
There are two major categories of COVID-19 diagnostic tests. Here’s what you need to know when deciding whether to take an at-home test or head to the doctor.
-
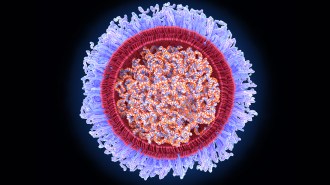 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineThese are the viruses that mRNA vaccines may take on next
Now that mRNA vaccines have proved effective against the coronavirus, scientists are taking aim at influenza, HIV and other viruses.
-
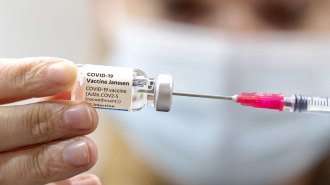 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineThe CDC recommends mRNA COVID-19 vaccines over J&J’s, citing fewer risks
Pfizer’s and Moderna's vaccines are more effective and cause fewer serious side effects than Johnson & Johnson’s jab, new data show.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineWhy it matters that health agencies finally said the coronavirus is airborne
Recognizing that the coronavirus spreads through the air reinforced the importance of wearing masks and altered public health recommendations.
-
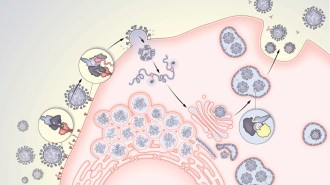 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineWhy the coronavirus’s delta variant dominated 2021
Mapping delta’s unique group of mutations and how they enhance the virus’s life cycle show why the variant spread so easily and caused so much havoc.
-
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyNeandertals were the first hominids to turn forest into grassland 125,000 years ago
Neandertals’ campfires, hunting and other activities altered the land over 2,000 years, making them the first known hominids to impact their environs.
By Bruce Bower -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineIn 2021, COVID-19 vaccines were put to the test. Here’s what we learned
Vaccines can’t single-handedly end the pandemic, but they are still essential in the fight against the coronavirus.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHow sleep may boost creativity
In a lab experiment, people who had fallen into a shallow sleep were more likely than non- or deep sleepers to later discover a sly math trick.
-
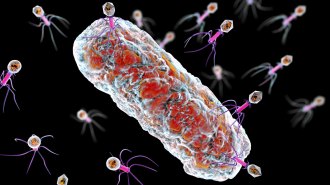 Microbes
MicrobesA bacteria-virus arms race could lead to a new way to treat shigellosis
As bacteria that cause shigellosis evolve to escape a virus, the microbes may become less deadly, a hopeful sign for “phage therapy.”
-
 Anthropology
Anthropology2021 research reinforced that mating across groups drove human evolution
Fossils and DNA point to mixing and mingling among Homo groups across vast areas.
By Bruce Bower -
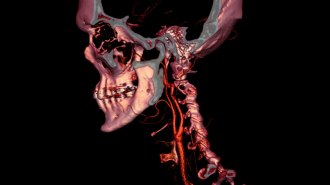 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineFor 50 years, CT scans have saved lives, revealed beauty and more
In 1971, the first CT scan of a patient laid bare the human brain. That was just the beginning of a whole new way to view human anatomy.