Humans
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyClovis hunters’ reputation as mammoth killers takes a hit
Early Americans’ stone points were best suited to butchering the huge beasts’ carcasses, scientists contend.
By Bruce Bower -
 Health & Medicine
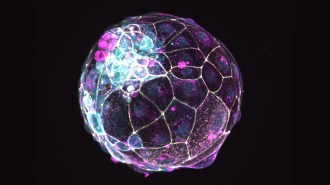
Health & Medicine‘Blastoids’ made of stem cells offer a new way to study fertility
Newly created “blastoids” could help with research on nonhormonal contraceptives and fertility treatments.
By Jake Buehler -
 Health & Medicine
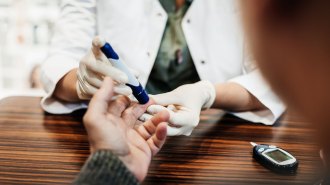
Health & MedicineThe coronavirus may cause fat cells to miscommunicate, leading to diabetes
Researchers are homing in on a surprising cause of high blood sugar in COVID-19 patients and possibly what to do about it.
-
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyArctic hunter-gatherers were advanced ironworkers more than 2,000 years ago
Swedish excavations uncover furnaces and fire pits from a big metal operation run by a small-scale society, a new study finds.
By Bruce Bower -
 Life
LifeHere are our favorite cool, funny and bizarre science stories of 2021
These are some of the fun science stories from this year that we couldn’t wait to talk about with friends.
-
 Space
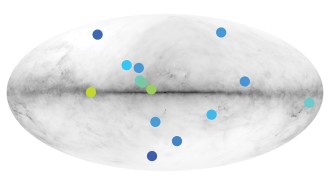
SpaceThese discoveries from 2021, if true, could shake up science
Discoveries in 2021, from hidden subatomic particles to the oldest animal fossils, could shake up science. But more evidence is needed to confirm them.
By Aina Abell -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineThe omicron variant is surging. Here’s what we’ve learned so far
Omicron is better at evading virus-attacking antibodies than previous coronavirus variants, but there are signs booster shots might help curb symptoms.
-
 Climate
ClimateVikings may have fled Greenland to escape rising seas
Vikings abandoned Greenland in the 15th century. Lower temperatures, an expanding ice sheet and rising sea levels may have played a role in their departure.
By Freda Kreier -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineCOVID-19 testing is complicated right now. Here are answers to 6 big questions
There are two major categories of COVID-19 diagnostic tests. Here’s what you need to know when deciding whether to take an at-home test or head to the doctor.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineThese are the viruses that mRNA vaccines may take on next
Now that mRNA vaccines have proved effective against the coronavirus, scientists are taking aim at influenza, HIV and other viruses.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineThe CDC recommends mRNA COVID-19 vaccines over J&J’s, citing fewer risks
Pfizer’s and Moderna's vaccines are more effective and cause fewer serious side effects than Johnson & Johnson’s jab, new data show.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineWhy it matters that health agencies finally said the coronavirus is airborne
Recognizing that the coronavirus spreads through the air reinforced the importance of wearing masks and altered public health recommendations.