Humans
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineJoggers naturally pace themselves to conserve energy even on short runs
Data from fitness trackers and treadmill tests challenge ideas about what drives speed.
By Chris Gorski -
 Health & Medicine
Health & Medicine50 years ago, scientists were seeking the cause of psoriasis
In the 1970s, scientists found a link between a chemical messenger and psoriasis, a complex inflammatory skin disorder.
-
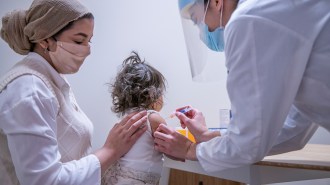 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineAntibiotics diminish babies’ immune response to key vaccines
With each round of antibiotics during a child’s first two years, antibody levels to four vaccines dropped further from what’s considered protective.
-
 Particle Physics
Particle PhysicsMuons spill secrets about Earth’s hidden structures
Tracking travel patterns of subatomic particles called muons helps reveal the inner worlds of pyramids, volcanoes and more.
-
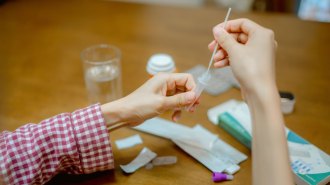 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineWhat experts told me to do after my positive COVID-19 at-home test
Rapid at-home tests mean many COVID-19 cases go unreported, but they’re a great tool for deciding when to leave isolation. I found that out firsthand.
By Anna Gibbs -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineWhy taking medications during pregnancy is so confusing
It's hard to know what new drugs are safe when medical research excludes pregnant people.
-
 Particle Physics
Particle PhysicsA new nuclear imaging prototype detects tumors’ faint glow
Nuclear imaging that relies on Cerenkov light could supplement standard-of-care technology for identifying location of tumors.
By Anna Gibbs -
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyThis hieroglyph is the oldest known record of the Maya calendar
Plaster fragments with the markings date to at least 200 B.C. and indicate that the calendar system, still used today, might be centuries older.
By Anna Gibbs -
 Anthropology
AnthropologyHow ancient, recurring climate changes may have shaped human evolution
Climate changes drove where Homo species lived over the last 2 million years, with a disputed ancestor giving rise to H. sapiens, a new study claims.
By Bruce Bower -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineWhat we learned about COVID-19 safety from a NYC anime convention
November’s Anime NYC convention was not a COVID-19 superspreader event, which means there are lessons to be learned.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineRacial bias can seep into U.S. patients’ medical notes
Black patients were more often described negatively in medical notes than white patients, which may impact care.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineWe can do better than what was ‘normal’ before the pandemic
With all that people have endured, it would be a missed opportunity to toss aside what we’ve learned from the COVID-19 pandemic.