Humans
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyAncient bacterial DNA hints Europe’s Black Death started in Central Asia
Archaeological and genetic data pin the origins of Europe’s 1346–1353 bubonic plague to a bacterial strain found in graves in Asia from the 1330s.
By Bruce Bower -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineNasal vaccines for COVID-19 offer hope and face hurdles
A squirt up the nose could reduce virus transmission, but like shots in the arm, the nasal vaccines have challenges to overcome.
-
 Anthropology
AnthropologyA new origin story for domesticated chickens starts in rice fields 3,500 years ago
Chickens, popular on today’s menus, got their start in Southeast Asia surprisingly recently, probably as exotic or revered animals, researchers say.
By Bruce Bower -
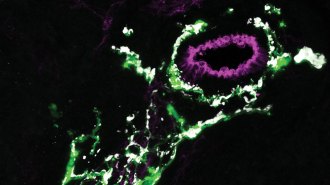 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceGlial cells may take on big jobs in unexpected parts of the body
Scientists are finding mysterious glia in the heart, spleen and lungs and wonder what they’re doing there.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineTrained dogs sniff out COVID-19 as well as lab tests do
Dogs can be trained to sniff out COVID-19 cases. They’re overall as reliable as PCR tests and even better at IDing asymptomatic cases, a study suggests.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineMissing COVID-19 data leave us in the dark about the current surge
Yankee Candle reviews and wastewater testing offer indirect hints, but we’re “flying blind,” says data expert Beth Blauer of Johns Hopkins University.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & Medicine4 answers to key questions about the monkeypox outbreak
Monkeypox has cropped up around the world, but it doesn’t spread easily like the coronavirus and most people probably don’t need to be concerned.
-
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyLasers reveal ancient urban sprawl hidden in the Amazon
South America’s Casarabe culture built a network of large and small settlements in what’s now Bolivia centuries before the Spanish arrived.
By Bruce Bower -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineUnexplained hepatitis cases in kids offer more questions than answers
There is a lot that is unclear about the hepatitis that’s impacting several hundred children worldwide, but parents shouldn’t panic.
-
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyCOVID-19 has killed a million Americans. Our minds can’t comprehend that number
We intuitively compare large, approximate quantities but cannot grasp such a big, abstract number as a million U.S. COVID-19 deaths.
By Sujata Gupta -
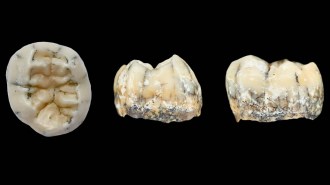 Anthropology
AnthropologyA Denisovan girl’s fossil tooth may have been unearthed in Laos
A molar adds to suspicions that mysterious hominids called Denisovans inhabited Southeast Asia's tropical forests.
By Bruce Bower -
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyPressure to conform to social norms may explain risky COVID-19 decisions
As a science reporter covering COVID-19, I knew I should mask up at Disney World. Instead, I conformed, bared my face and got COVID-19.
By Sujata Gupta