Humans
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicinePersonalized ‘prehabilitation’ helps the body brace for major surgery
A small study finds that individualized prehab can dampen harmful immune responses and may reduce complications after an operation.
By Anna Gibbs -
 Humans
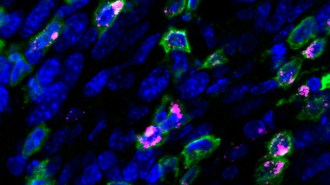
HumansA therapeutic HPV vaccine shrank cervical tumors in mice
An HPV vaccine delivered into the nose can treat cervical tumors in mice. The vaccine targets a cancer protein produced by the virus.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Health & Medicine
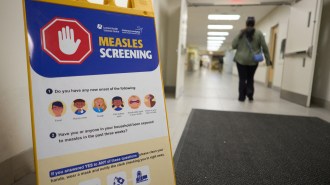
Health & MedicineCanada just lost its measles elimination status. Is the U.S. next?
Canada has had more than a year of continuous measles transmission. The United States has until January to limit cases before losing status.
-
 Anthropology
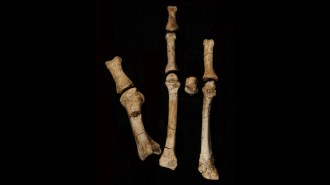
AnthropologyA foot fossil suggests a second early human relative lived alongside Lucy
Foot bones and other fossils have been attributed to Australopithecus deyiremeda, a recently discovered species that may shake up the human family tree.
By Jay Bennett -
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyGratitude can increase joy, even if it feels a little cringe
Like exercise, gratitude takes many forms. Finding the right practice, research shows, is up to the individual.
By Sujata Gupta -
 Health & Medicine
Health & Medicine‘Butt breathing’ could help people who can’t get oxygen the regular way
Takanori Takebe’s strange investigation into whether humans can use the gut for breathing has surprisingly sentimental origins: helping his dad.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & Medicine3,000 steps per day might slow Alzheimer’s disease
In people at risk for Alzheimer’s disease, researchers linked minimal to moderate physical activity to a 3-to 7-year delay in cognitive symptoms.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineBuilding a better skin barrier
Skin is a barrier meant to keep small invaders out. Products making their way across it should boost that mission.
By Anna Gibbs -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineA diet low in glutamate may ease migraines
People with Gulf War Illness found relief from migraines after a month on a low-glutamate diet, hinting at a new way to ease symptoms.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicinemRNA flu vaccines are making their way through clinical trials
The mRNA platform offers the advantage of faster vaccine production, which could allow more time to decide on which flu strains to cover.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineIn animal tests, this needle-free insulin acted as fast as injections
Managing diabetes with injections is challenging. Joining insulin to a skin-penetrating polymer was as effective as shots at regulating blood sugar.
By Simon Makin -
 Health & Medicine
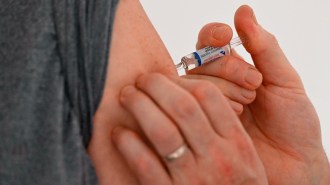
Health & MedicineEroding access to childhood vaccines jeopardizes health for all
Recent U.S. decisions about vaccines signal bigger changes to come that could threaten the foundation of the national childhood immunization schedule.