Humans
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsBlack Death immunity came at a cost to modern-day health
A genetic variant that boosts Crohn’s disease risk may have helped people survive the 14th century bubonic plague known as the Black Death.
By Wynne Parry -
 Psychology
PsychologyThe pandemic shows us how crises derail young adults’ lives for decades
Age matters for when we experience calamities, such as pandemics. Young adults are especially vulnerable to getting thrown off their life course.
By Sujata Gupta -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineA swarm of sneaky omicron variants could cause a COVID-19 surge this fall
Scientists are tracking similar mutations showing up in many variants that help the coronavirus evade some of our immune defenses and treatments.
-
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyDrone photos reveal an early Mesopotamian city made of marsh islands
Urban growth around 4,600 years ago, near what is now southern Iraq, occurred on marshy outposts that lacked a city center.
By Bruce Bower -
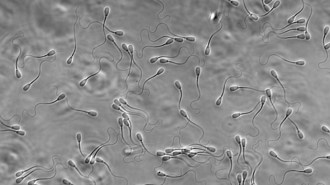 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineCooperative sperm outrun loners in the mating race
Sperm that swim in clusters travel more directly toward the uterus, while overcoming fluid currents in the reproductive tract.
-
 Humans
HumansHere’s where jazz gets its swing
Swing, the feeling of a rhythm in jazz music that compels feet to tap, may arise from near-imperceptible delays in musicians’ timing, a study shows.
By Nikk Ogasa -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineLosing amphibians may be tied to spikes in human malaria cases
Missing frogs, toads and salamanders may have led to more mosquitoes and potentially more malaria transmission, a study in Panama and Costa Rica finds.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & Medicine‘Breathless’ explores COVID-19’s origins and other pandemic science
In his new book, David Quammen examines what we’ve learned about SARS-CoV-2 and puts the pandemic in the context of previous coronavirus scares.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineGenetics of human evolution wins 2022 Nobel Prize in physiology or medicine
By figuring out how to extract DNA from ancient bones, Svante Pääbo was able to decipher the genomes of our hominid relatives.
By Tina Hesman Saey and Aimee Cunningham -
 Humans
HumansHow to get a crying baby to sleep, according to science
Science has come up with a recipe for lulling a crying baby to sleep: Carry them for five minutes, sit for at least five more and then lay them down.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineChristopher Barnes is on a quest for a universal coronavirus vaccine
Christopher Barnes wants to stop the viruses that cause COVID-19, the common cold and more.
-
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyBig questions inspire the scientists on this year’s SN 10 list
These scientists to watch study climate change, alien worlds, human evolution, the coronavirus and more.