Humans
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyThe oldest scaled-down drawings of actual structures go back 9,000 years
Rock engravings in Jordan and Saudi Arabia may be maps or blueprints of desert kites, massive structures once used to capture animal herds.
By Bruce Bower -
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyAnténor Firmin challenged anthropology’s racist roots 150 years ago
In The Equality of the Human Races, Haitian scholar Anténor Firmin showed that science did not support division among the races.
By Sujata Gupta -
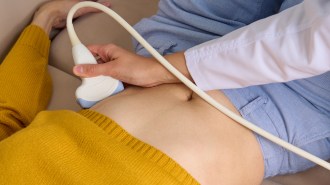 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineStimulating spleens with ultrasound hints at a treatment for inflammation
Using an intense kind of ultrasound stimulation against inflammation holds promise but so far has been tested only in rodents and human blood samples.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineScientists may have found an antidote for death cap mushrooms
A dye countered the effects of a mushroom toxin in human cells and mice. If the antidote does the same in people, it has potential to save lives.
-
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyDeliberate ignorance is useful in certain circumstances, researchers say
The former East German secret police, the Stasi, spied on people for years. But when given access to the Stasi files, most people didn’t want to read them, researchers found.
By Sujata Gupta -
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceA rare mutation helped one man stave off Alzheimer’s for decades
The brain of a Colombian man with an inherited form of Alzheimer’s may hint at ways to halt or slow the progression of the disease.
By Simon Makin -
 Space
Space50 years ago, cosmic rays may have caused Apollo astronauts to see lights
Apollo astronauts reported seeing flashes of light where there were none. Fifty years later, the flashes still mess with modern astronauts’ vision.
-
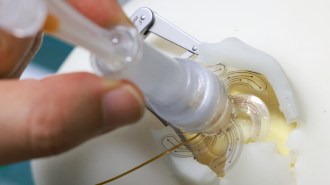 Tech
TechA flower-shaped soft robot could make brain monitoring less invasive
Once inserted in the skull, the device unfurls flexible sensors that can monitor the brain's electrical activity less invasively than current methods.
By Bob Hirshon -
 Life
LifeThe new human pangenome could help unveil the biology of everyone
The deciphered DNA includes never-before-explored parts of the genome and better represents the genetic diversity of all humans.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineSan Francisco airport will monitor plane waste for COVID-19 variants
The airport, working with the CDC and a biotech company, will be the first in the United States to regularly test plane sewage.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & Medicine50 years ago, enzyme injections showed promise for treating a rare disease
Enzyme replacement can offer relief to people with rare diseases. Now, scientists have found a way to treat one disease before a person is even born.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineWHO declares an end to the global COVID-19 public health emergency
Global COVID-19 deaths are down and immunity is up. But with the virus here to stay, it’s time to shift to more long-term health measures.