Humans
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Life
LifeIn Australia, mosquitoes and possums may spread a flesh-eating disease
Field surveys show that genetically identical bacteria responsible for a skin disease called Buruli ulcer appear in mosquitos, possums and people.
-
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyHow Asia’s first nomadic empire broke the rules of imperial expansion
New studies reveal clues to how mobile rulers assembled a multiethnic empire of herders known as the Xiongnu more than 2,000 years ago.
By Bruce Bower -
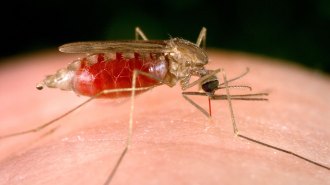 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineFour things to know about malaria cases in the United States
Five people have picked up malaria in the United States without traveling abroad. The risk of contracting the disease remains extremely low.
-
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyIndigenous input revealed early hints of fiber making in the tropics
To decipher marks on nearly 40,000-year-old stone tools and figure out what they were used for, researchers turned to the Philippines’ Pala’wan people.
-
 Psychology
PsychologyBoys experience depression differently than girls. Here’s why that matters
Boys’ depression often manifests as anger or irritability, but teen mental health surveys tend to ask about hopelessness.
By Sujata Gupta -
 Anthropology
AnthropologyFossil marks suggest hominids butchered one another around 1.45 million years ago
Researchers disagree whether new evidence of stone tool marks on a hominid leg bone reflects ancient cannibalism or perhaps some other, undetected behavior.
By Bruce Bower -
 Astronomy
Astronomy50 years ago, a search for proof that the Maya tracked comets came up short
The mystery of whether the ancient civilization tracked comets endures, but recent evidence hints the Maya tracked related meteor showers.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsThe first gene therapy for muscular dystrophy has been approved for some kids
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration cleared a shortened version of a gene for a muscle protein to be used in 4- and 5-year-olds with muscular dystrophy.
-
 Tech
TechHow understanding horses could inspire more trustworthy robots
Computer scientist Eakta Jain pioneered the study of how human-horse interactions could help improve robot design and shape human-robot interactions.
-
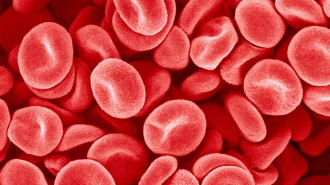 Health & Medicine
Health & Medicine‘In the Blood’ traces how a lifesaving product almost didn’t make it
There’s plenty of drama in Charles Barber’s new book, which explores why a blood-clotting invention was initially dismissed.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyAn old perfume bottle reveals what some ancient Romans smelled like
Chemical analyses reveal that an unopened flask of perfume from 2,000 years ago contained patchouli, a common ingredient in modern perfumes.
-
 Anthropology
AnthropologyThese ancient flutes may have been used to lure falcons
Seven bird-bone flutes unearthed from a site in northern Israel are about 12,000 years old and may have been used as bird calls.
By Sid Perkins