Humans
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Health & Medicine
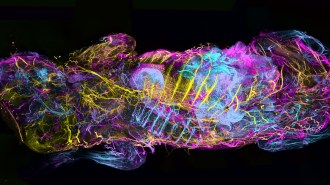
Health & MedicineWith a new body mapping technique, mouse innards glow with exquisite detail
Removing cholesterol from mouse bodies lets fluorescently labeled proteins infiltrate every tissue, helping researchers to map entire body systems.
-
 Psychology
PsychologyTime in nature or exercise is touted for happiness. But evidence is lacking
A review of hundreds of studies finds limited strong scientific evidence to support many common recommendations for leading a happier life.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & Medicine‘Milking’ umbilical cords may help some sickly newborns
Taking a few seconds to push umbilical cord blood into a baby’s belly could provide extra essential nutrients. But questions about the practice remain.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineIron deficiency goes unnoticed in too many U.S. female adolescents
Low iron causes problems from dizziness to severe anemia. It’s time to reevaluate screening guidelines to catch the problem earlier, an expert argues.
By Skyler Ware -
 Chemistry
ChemistryHow Benjamin Franklin fought money counterfeiters
Researchers are confirming some of the techniques that Benjamin Franklin and his associates used to help early American paper currency succeed.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineNew Alzheimer’s drugs are coming. Here’s what you need to know
Several new drugs that target brain plaques slow mental decline in people with Alzheimer’s disease. But they are not for everyone, researchers caution.
-
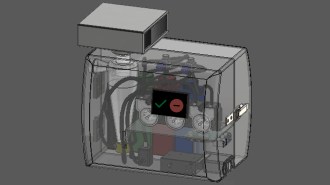 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineA new device can detect the coronavirus in the air in minutes
The detector can sense as a few as seven to 35 coronavirus particles per liter of air — about as sensitive as a PCR test but much quicker.
-
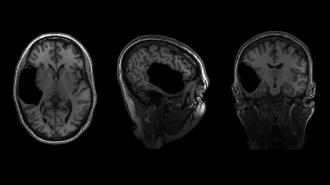 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceElyse G.’s brain is fabulous. It’s also missing a big chunk
A new project explores interesting brains to better understand neural flexibility.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Earth
EarthWildfires aren’t going away. Here’s how smoke can affect your health
How does repeat exposure to wildfire smoke affect our health? Three experts weigh in on the massive air pollution fueled by Canada’s ongoing fires.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Humans
HumansLauren Schroeder looks beyond natural selection to rethink human evolution
Paleoanthropologists studying the fossil record have long focused on natural selection, but other processes play a big role too.
By Anna Gibbs -
 Health & Medicine
Health & Medicine50 years ago, scientists thought coffee might treat hyperactivity
Decades of follow-up research into whether caffeine can treat the symptoms of kids with ADHD has come up with more questions than answers.
By Aina Abell -
 Psychology
Psychology‘Fires in the Dark’ illuminates how great healers ease mental suffering
Kay Redfield Jamison’s new book examines approaches used throughout history to restore troubled minds and broken spirits.
By Bruce Bower