Humans
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsA new look at Ötzi the Iceman’s DNA reveals new ancestry and other surprises
Ötzi had genetic variants for male-pattern baldness and dark skin, and he also had an unusual amount of early farmer ancestry, a new DNA analysis finds.
-
 Physics
PhysicsHow to run a marathon in under two hours
Running between other people reduces air resistance. A new study identifies optimal positioning of such drafting formations. Watch out, marathon records.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceNeuroscientists decoded a Pink Floyd song using people’s brain activity
The technique could be used to improve devices that allow communication from people unable to speak.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineWhy are more people under 50 getting colorectal cancer? Scientists have some clues
Science News spoke with doctors about their research into early-onset colorectal cancer. Here’s what they’re learning and what questions remain.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Climate
ClimateExtreme heat taxes the body in many ways. Here’s how
Climate change is bringing longer, humid heat waves and hotter nights. Here's how our bodies try to beat the heat and what happens when they can't.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineClimate change puts children’s health at risk now and in the future
Heat waves, wildfires and other climate-related effects on the environment are particularly hard on children’s physical and mental health.
-
 Health & Medicine
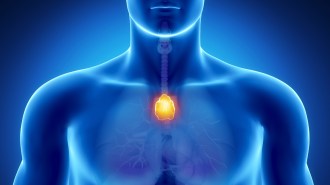
Health & MedicineThe thymus withers away after puberty. But it may be important for adults
The thymus is considered somewhat unnecessary in adults. But a new study finds that its removal is associated with heightened risks of death and cancer.
-
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyA child’s ornate necklace highlights ancient farmers’ social complexity
The intricate necklace, reconstructed by researchers, was found on the remains of a child buried about 9,000 years ago in a Middle Eastern village.
By Bruce Bower -
 Health & Medicine
Health & Medicine‘Blight’ warns that a future pandemic could start with a fungus
‘The Last of Us’ is fiction, but the health dangers posed by fungi are real, a new book explains.
-
 Archaeology
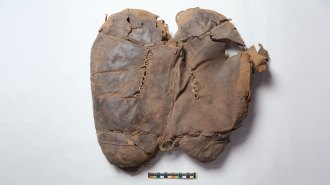
ArchaeologyThe oldest known horseback riding saddle was found in a grave in China
The well-used saddle, dated to more than 2,400 years ago, displays skilled leather- and needlework. Its placement suggests its owner was on a final ride.
By Bruce Bower -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineMany sports supplements have no trace of their key ingredients
A chemical analysis of 57 supplements found that 40 percent had undetectable amounts of key ingredients. Only 11 percent had accurate amounts.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Humans
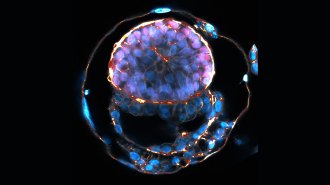
HumansHuman embryo replicas have gotten more complex. Here’s what you need to know
Lab-engineered human embryo models created from stem cells provide a look at development beyond the first week. But they raise ethical questions.