Humans
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsMost of today’s gene therapies rely on viruses — and that’s a problem
The next big strides in gene therapy for rare diseases may come from CRISPR and new approaches to delivery.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineBlocking an aging-related enzyme may restore muscle strength
Treating old mice with a drug that inhibits a “gerozyme” restored muscle strength, which can diminish with aging.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineNewly identified stem cells can lure breast cancer to the spine
A new type of stem cell discovered in mice and humans might explain why cancer that spreads to other body parts preferentially targets the spine.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceWhat a look at more than 3,000 kinds of cells in the human brain tells us
A wide-reaching look at the cells that build the brain, detailed in 21 studies, showcases the brain’s cellular diversity and clues about how it works.
-
 Archaeology
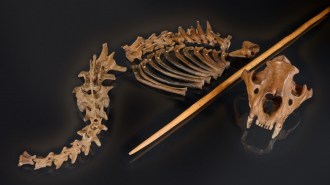
ArchaeologyNeandertals hunted cave lions at least 48,000 years ago
A new study reports the first direct evidence of Neandertals slaying the big cats, and the earliest evidence of any hominids killing a large predator.
By Bruce Bower -
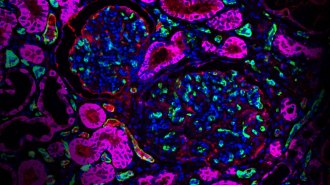 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineA monkey survived two years with a miniature pig’s kidney
A new study is the latest in a string of efforts seeking to use other animal species to solve the global organ shortage in people.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyHuman footprints in New Mexico really may be surprisingly ancient, new dating shows
Two dating methods find that human tracks in White Sands National Park in New Mexico are roughly 22,000 years old, aligning with a previous estimate.
-
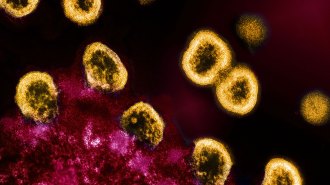 Health & Medicine
Health & Medicine‘Dormant’ HIV has ongoing skirmishes with the body’s immune system
In people on HIV drugs, defective viral bits may still exhaust T cells, possibly making it harder to fight back if people go off the drugs.
By John Carey -
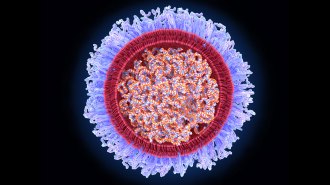 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineEarly mRNA research that led to COVID-19 vaccines wins 2023 medicine Nobel Prize
Biochemists Katalin Karikó and Drew Weissman devised mRNA modifications to make vaccines that trigger good immune responses instead of harmful ones.
-
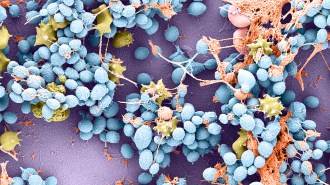 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHow a deadly fungus is so good at sticking to skin and other surfaces
One of Candida auris’ scary superpowers is its stick-to-itiveness. Unlike other fungi, the pathogen uses electrical charges to glom onto things.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHere’s how much coronavirus people infected with COVID-19 may exhale
Just breathing naturally can lead people with COVID-19 to emit dozens of copies of viral RNA a minute and that can persist for eight days, a study finds.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineMouth taping may be a trending sleep hack, but the science behind it is slim
Mouth taping is big on social media, but few studies have evaluated it. Some evidence suggests that sealing the lips shut may help people with sleep apnea.
By Meghan Rosen