Humans
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Neuroscience
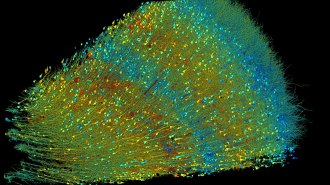
NeuroscienceBiological puzzles abound in an up-close look at a human brain
Mirror-image nerve cells, tight bonds between neuron pairs and surprising axon swirls abound in a bit of gray matter smaller than a grain of rice.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineYoung people’s use of diabetes and weight loss drugs is up 600 percent
Young people’s use of diabetes and weight loss drugs like Ozempic and Wegovy is surging, especially among females ages 18 to 25.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceTwo distinct neural pathways may make opioids like fentanyl so addictive
A study in mice looked at how feelings of reward and withdrawal that opioids trigger play out in two separate circuits in the brain.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHuman body lice could harbor the plague and spread it through biting
Rats and fleas previously got all the blame, but humans’ own parasites could be involved.
-
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyOne of the world’s earliest farming villages housed surprisingly few people
Hundreds, not thousands, occupied the Turkish site of Çatalhöyük nearly 9,000 years ago, undermining arguments for a Neolithic social revolution.
By Bruce Bower -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineBurning the stomach lining reduces the ‘hunger hormone’ and cuts weight
An experimental weight loss procedure blasts the stomach lining with heat to curb hunger and cut pounds.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineGenetic analyses of the bird flu virus unveil its evolution and potential
The H5N1 outbreak in cattle is giving flashbacks to the COVID pandemic. But this time is different.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineExtreme heat will put millions more older adults at risk in the future
By 2050, as many as an additional 246 million adults 69 and older could experience temperature extremes that exceed 37.5° Celsius.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineCows might host both human and bird flus
Both kinds of influenza viruses may break into cattle cells using receptors similar to those in people, wild birds and poultry.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineA new gel stops mice from getting too drunk
The iron-milk substance can break down alcohol fast and protect against liver damage in mice. Scientists hope to test the gel in people next.
-
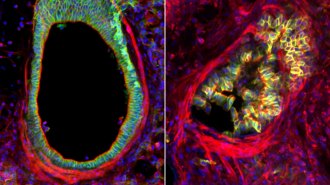 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineChronic asthma could be caused by cell overcrowding in the airways
Identifying drugs to reduce the excessive expulsion of cells in the lung lining could reduce the damage of chronic asthma.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & Medicine50 years ago, phantom pain was blamed on misfiring nerves
Researchers now know that the cause of post-amputation pain is more complex, which is leading to new treatments.