Humans
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Anthropology
AnthropologyAncient DNA unveils a previously unknown line of Neandertals
DNA from a partial skeleton found in France indicates that European Neandertals consisted of at least two genetically distinct populations.
By Bruce Bower -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineCalifornia droughts may help valley fever spread
Droughts temporarily dampen the number of valley fever cases across the state, but cases spike in the years after rains return.
-
 Health & Medicine
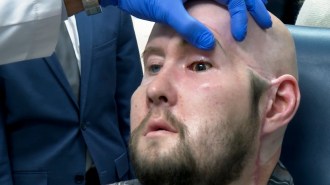
Health & MedicineThe first face transplant to include an eye shows no rejection a year later
A man who received a partial face transplant that included an eye can’t see out of the eye, but there is blood flow to it.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & Medicine50 years ago, some of plastic’s toxic hazards were exposed
Worker exposure to vinyl chloride became tightly regulated after the chemical was linked with liver cancer. Now, its use may be on the chopping block.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineA new drug shows promise for hot flashes due to menopause
Two clinical trials found that the nonhormonal drug elinzanetant eased hot flashes and improved sleep, two common menopause symptoms.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineA next-gen pain drug shows promise, but chronic sufferers need more options
A new painkiller nearing approval called suzetrigine may prove to be an opioid alternative. But for many with chronic pain, treatment must go beyond pills.
-
 Health & Medicine
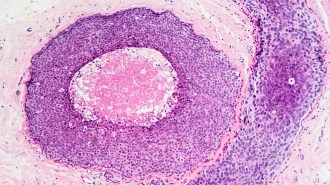
Health & MedicineWhat is ‘Stage 0’ breast cancer and how is it treated?
Actress Danielle Fishel's diagnosis has raised awareness of a condition that affects about 50,000 U.S. women annually.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicinePeople with food and other allergies have a new way to treat severe reactions
A new epinephrine nasal spray gives people a needle-free way to treat severe allergic reactions to food, insect venom and drugs.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineExtreme heat and rain are fueling rising cases of mosquito-borne diseases
Extreme Climate Update looks at the perfect storm climate change is creating for mosquitoes and the diseases they carry, like dengue and West Nile.
-
 Microbes
MicrobesMore than 100 bacteria species can flourish in microwave ovens
Swabs of 30 microwave ovens in different settings identified over 100 bacterial species, some of which could be pathogenic or cause food-borne disease.
-
 Health & Medicine
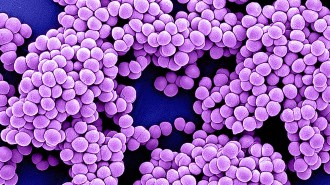
Health & Medicine50 years ago, antibiotic resistant bacteria became a problem outside hospitals
Infections from drug-resistant bacteria have skyrocketed over the last 50 years. Now, new technologies could help doctors save lives.
-
 Health & Medicine
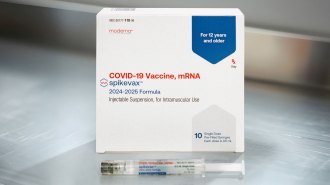
Health & MedicineNew COVID-19 booster shots have been approved. When should you get one?
The vaccines target the omicron variants currently circulating in the United States.
By Tina Hesman Saey and Meghan Rosen