Humans
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Anthropology
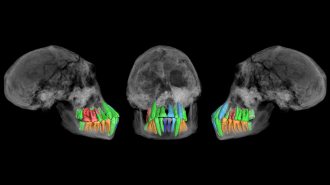
AnthropologyFossil teeth hint at a surprisingly early start to humans’ long childhoods
Signs of temporarily delayed tooth development in the skull of an ancient Homo species youth spark debate about the origins of humanlike growth.
By Bruce Bower -
 Anthropology
AnthropologyHow does a fossil become a superstar? Just ask Lucy.
Geologic good fortune, skilled scientific scrutiny and a catchy name turned Lucy into an evolutionary icon.
By Bruce Bower -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineThe virus behind an outbreak in Brazil can spread from mother to fetus
Transmission of Oropouche virus to the womb has been confirmed in two stillbirths and one birth with congenital anomalies that occurred in Brazil.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineA twisted protein sheds light on chronic wasting disease in deer
The detailed structure of a misfolded protein from a diseased deer could help explain why the disease hasn’t made the leap to humans.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsA common drug may help treat a rare genetic disease
Ibuprofen counters problems caused by mutations in the MAN1B1 gene, fruit fly tests show. Early results in three children are ”fairly positive.”
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & Medicine‘The Power of Prions’ explores misfolded proteins’ role in brain diseases
Michel Brahic’s new book spotlights prions’ role in diseases such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyA digital exam reels in engraved scenes of Stone Age net fishing
Nearly 16,000-year-old portrayals of fish surrounded by nets had evaded detection until a new technique took magnification to a new level.
By Bruce Bower -
 Archaeology
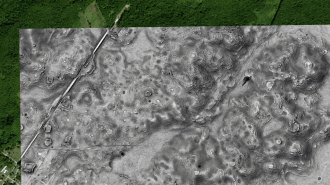
ArchaeologyA huge, ancient Maya city has been found in southern Mexico
Lasers revealed that the city spanned roughly the same area as Beijing and may have been among the most densely populated in the region.
-
 Anthropology
AnthropologyThe ‘midlife crisis’ is too simple a story, scientists say
Some scientists want to shift focus to the teen mental health crisis. But the course of happiness is too complex for simplistic theories, experts warn.
By Sujata Gupta -
 Humans
HumansA phone app could help people have lucid dreams
New experiments show that an app developed by researchers can boost snoozing users’ likelihood of knowing when they are having a dream.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineWhy finding bird flu in a U.S. pig for the first time is raising new worries
Swine can act as so-called “mixing vessels” for human and bird flus, giving avian viruses an opportunity to adapt for spreading in people.
-
 Psychology
PsychologySmiles tweaked by AI can boost attraction, a speed-dating study shows
Using face filters to alter expressions manipulated feelings of attraction, raising questions about how such technology may influence social interactions.