Humans
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Psychology
PsychologyRatio for a good life exposed as ‘nonsense’
A heralded calculation of people’s ability to flourish is a mathematical mirage, researchers say.
By Bruce Bower -
 Humans
HumansDNA reveals details of the peopling of the Americas
Migrants came in three distinct waves that interbred once in the New World.
-
 Tech
TechOnline ‘likes’ multiply themselves
Social media users swayed by previous ratings, researchers find when they randomly assign positive and negative votes.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineCamels implicated as possible hosts of MERS virus
Antibodies to a mysterious pathogen that has sickened 94 people were found in camels in Oman and the Canary Islands.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineVaccine protects against malaria in early test
A series of shots enables volunteers to fend off a live infection by the disease-causing parasite.
By Nathan Seppa -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHigh blood glucose levels linked to dementia
Elderly people with elevated blood glucose levels are more apt to develop dementia, whether or not they have diabetes.
By Nathan Seppa -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineSpace-mapping neurons found in human brain
Grid cells may orient people in Euclidean space.
-
 Humans
HumansY chromosome analysis moves Adam closer to Eve
A pair of genetic studies has pushed back age of men's most recent common ancestor.
By Erin Wayman -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineGoing out to lunch zaps mental focus
Sharing a midday meal with friends could lead later to errors at work.
-
 Anthropology
AnthropologyMummified Incan teen drank, did drugs
Girl, who was sacrificed, may have been sedated by alcohol, coca leaves.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineFull moon may mean less sleep
Slumber waxes and wanes along with lunar rhythm, researchers find with people sleeping in windowless lab.
-
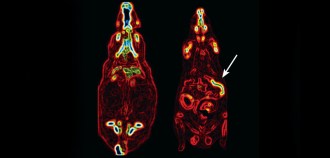 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineGastric bypass surgery causes sugar-burning gut growth in rats
The rapid improvement in symptoms of diabetes, seen in patients before weight loss begins, may be due to changes in part of the intestine.
By Meghan Rosen