Humans
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineAntibodies show progress against HIV
Proteins suppress disease in monkeys, but don’t cure it.
By Nathan Seppa -
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceMining mouse movements to make more meds
Animal models are a great way to look at psychoactive drugs and how they work. A new paper purports to simplify it all down to one test.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineDon’t buy breast milk on the Internet, and other helpful tips
A new study finds bacterial contamination in breast milk bought online, but there’s more to the story than that.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsGenetic variants may keep Siberians warm
People in frigid cold evolved changes in fat metabolism, shivering.
-
 Environment
EnvironmentPolluted water interferes with drug that combats parasitic scourge
Arsenic contamination fuels resistance to one treatment for leishmaniasis.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineGene links smoking, multiple sclerosis
Smokers with genetic variant face tripled risk of MS.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineNew definition of ‘full term’ narrows on-time arrival window
Until now, babies born at any time during a wide five-week window were considered fully cooked. Now, a panel of clinicians says otherwise.
-
 Humans
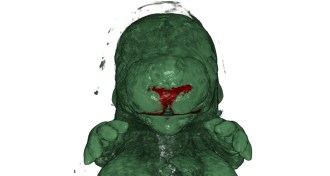
HumansWhat makes a face go round
Genetic enhancers acting far away from their intended genes can help shape a face during development.
-
 Health & Medicine
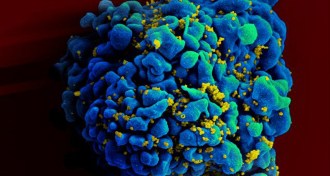
Health & MedicineInactive HIV poses even greater barrier to cure
The reservoir of dormant virus strains is larger than scientists estimated, a finding that could make the virus harder to combat.
By Science News -
 Psychology
PsychologyGroups recall travel details better than loners
Small teams of people can recite key information from public announcements better than any one person.
By Bruce Bower -
 Anthropology
AnthropologyHunting boosts lizard numbers in Australian desert
Reptiles prefer to live in places aboriginal people have burned.
-
 Humans
HumansOur Final Invention
Computers already make all sorts of decisions for you. Imagine if the machines controlled even more aspects of life and could truly think for themselves.
By Sid Perkins