Humans
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Anthropology
AnthropologyCancer proposed as spur for evolution of dark-skinned ancestors
Fatal ailments might have sparked DNA changes that yielded dark skin in human ancestors.
By Bruce Bower -
 Environment
EnvironmentHandling receipts increases exposure to BPA
People who handle cash register receipts printed on thermal paper show notable exposure to bisphenol A.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineBeating addiction: impossible or surprisingly common?
Addiction may be a dysfunctional if temporary coping strategy, clouds may not reduce global warming and other stories from the March 22 issue.
By Eva Emerson -
 Health & Medicine
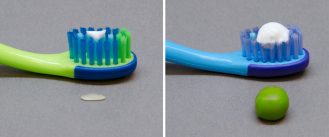
Health & MedicineBrush kids’ teeth with just a little fluoride toothpaste
The American Dental Association has released new brushing guidelines for infants.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineCamels in Saudi Arabia teeming with MERS virus
Three-quarters of animals tested had signs of the MERS virus, which can be deadly in people.
By Beth Mole -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineAcetaminophen use in pregnancy linked to kids’ slightly higher risk of ADHD
A large analysis shows an association between acetaminophen use in pregnancy and slightly higher risks of ADHD, but it does not prove the pain reliever causes the disorder.
By Nathan Seppa -
 Health & Medicine
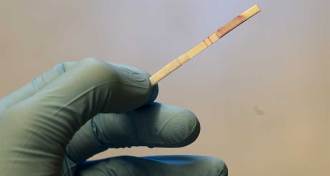
Health & MedicineUrine test detects not pregnancy but cancer
A paper strip uses nanoparticles to pick up evidence of tumors or blood clots in mice.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Psychology
PsychologyBeatles reaction puzzles even psychologists
From the February 29, 1964, issue: Psychologists are as puzzled as parents over the explosive effect the Beatles are having on American teen-agers.
-
 Environment
EnvironmentLegionnaires’ disease bacteria lurk in tap water
Found in nearly half of faucets, contamination could explain sporadic cases of disease.
By Beth Mole -
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyAlternatives needed to do-it-yourself feces swaps
Three researchers are calling for the FDA to regulate feces as a human tissue rather than a drug to make it easier for doctors to perform fecal transplants.
-
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyFire used regularly for cooking for 300,000 years
Israeli cave yields a fireplace where Stone Age crowd may have cooked up social change.
By Bruce Bower -
 Psychology
PsychologyLend an ear to science
Pop music hit maker Clive Davis knows a catchy song when he hears one. Now an app aims to define that elusive quality more concretely.