Humans
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineBereavement can take toll on health, not just emotions
In the month after a partner dies, spouse more prone to heart attack, stroke.
By Nathan Seppa -
 Psychology
PsychologySuicide rates drop in big cities
With more social connections, people may be less inclined to take their own lives.
By Meghan Rosen -
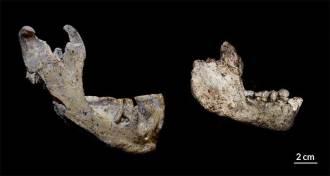 Anthropology
AnthropologyHuman ancestors at West Asian site deemed two species
Researchers see two species instead of one at oldest known Homo site outside Africa.
By Bruce Bower -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineExperimental drug no Methuselah formula
Compound lets mice live healthier lives but doesn't extend life span.
-
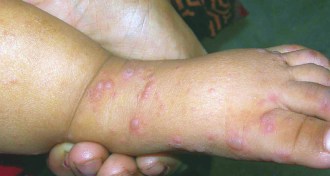 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineExperimental vaccines protect children from hand, foot and mouth disease
Shots prevented cases resulting from enterovirus 71.
By Nathan Seppa -
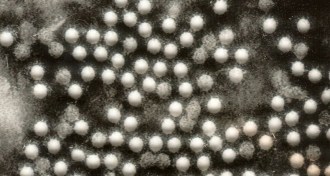 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineFive California children have polio-like symptoms
At least five, and possibly as many as 25, children in California have experienced poliolike symptoms, including paralysis of limbs and breathing problems, since 2012. Scientists are not yet sure what is causing the emerging disease.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineRabbit heart gets full electrode jacket
A silicon jacket makes it possible for scientists to place sensors on specific areas of the heart without glue or stitches and could one day be used for diagnosing and treating human heart diseases.
-
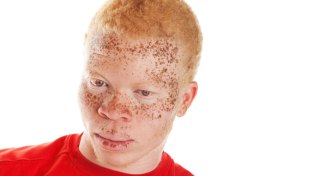 Anthropology
AnthropologyCancer proposed as spur for evolution of dark-skinned ancestors
Fatal ailments might have sparked DNA changes that yielded dark skin in human ancestors.
By Bruce Bower -
 Environment
EnvironmentHandling receipts increases exposure to BPA
People who handle cash register receipts printed on thermal paper show notable exposure to bisphenol A.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineBeating addiction: impossible or surprisingly common?
Addiction may be a dysfunctional if temporary coping strategy, clouds may not reduce global warming and other stories from the March 22 issue.
By Eva Emerson -
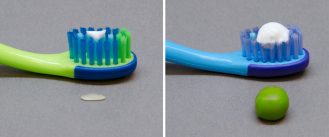 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineBrush kids’ teeth with just a little fluoride toothpaste
The American Dental Association has released new brushing guidelines for infants.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineCamels in Saudi Arabia teeming with MERS virus
Three-quarters of animals tested had signs of the MERS virus, which can be deadly in people.
By Beth Mole