Humans
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineObesity on the rise globally
Some 2.1 billion people, almost 30 percent of the world’s population, are overweight or obese.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & Medicine‘Bionic’ pancreas shows promise in diabetes test
Tests of a “bionic pancreas” confirm that the wearable devices can maintain blood glucose levels without the need for finger pricks or insulin shots in patients with type 1 diabetes.
-

-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineMammography’s limits becoming clear
It may be time to move way from blanket recommendations about mammography and empower women to decide for themselves, new work suggests.
By Laura Beil -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineIf timing’s right, cats and roaches may be good for kids’ allergies
Exposure to mice, roaches and cats before a child’s first birthday may confer protection against asthma and allergies, a new study suggests.
-
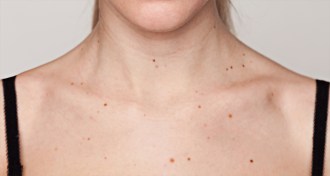 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineNumber of skin moles tied to breast cancer risk
Women who have many moles also have increased disease risk, which may reflect higher estrogen levels.
By Nathan Seppa -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineBacteria linked to stress-induced heart attacks
Bacteria may play an underlying role in heart attacks brought on by stress.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineAnesthesia linked to effects on children’s memory
Undergoing anesthesia as an infant may impair a person's ability to recall details later in life, a new study suggests.
-
 Humans
HumansThere’s more to acing interviews than holding the vocal fry
A new study of vocal fry, a low razz in human speech, suggests job interviewees might want to hold the fry. But there's more to a job interview than a little vocal sizzle.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceStem cell approach for Parkinson’s disease gets boost
Postmortem study finds Parkinson’s patients can retain transplanted neurons for years.
-
 Psychology
PsychologyWhy stabbing a voodoo doll is so satisfying
To measure how aggressive a person is, psychologists turn to voodoo dolls and hot sauce.
-
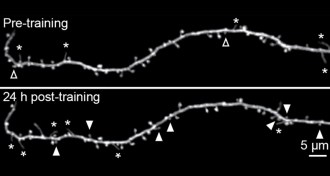 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceSleep strengthens some synapses
Mice show signs of stronger neuron connections when allowed to sleep after learning a trick.