Humans
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineBabies are kinder after you dance with them
Babies who grooved in sync with an adult were more likely to be little helpers later.
-
 Health & Medicine
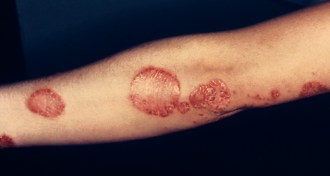
Health & MedicineTwo genes clear up psoriasis and eczema confusion
Psoriasis and eczema are often mistaken for each other, leading to mistreatment. Testing just two genes could eliminate this confusion.
By Nsikan Akpan -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineYet another reason to hate ticks
Ticks are tiny disease-carrying parasites that should also be classified as venomous animals, a new study argues.
-
 Quantum Physics
Quantum PhysicsQuantum math makes human irrationality more sensible
Vagaries of human decision making make sense if quantum math describes the way the brain works.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineMold behind 2013 yogurt recall may cause disease
Genome sequencing links a new, virulent strain of mold to the 2013 Chobani yogurt recall.
-
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyMain result of Facebook emotion study: less trust in Facebook
Facebook’s controversial manipulation of emotional posts raises key questions about how to study online behavior.
By Bruce Bower -
 Psychology
PsychologyPeople will take pain over being left alone with their thoughts
Evidence suggests that people dislike solitary thought so much that some prefer electric shocks.
By Bruce Bower -
 Psychology
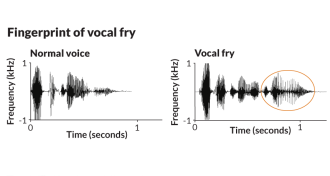
PsychologyVocal fry
At the lowest registers of the human voice, a creaky, popping sound known as vocal fry emerges.
-
 Health & Medicine
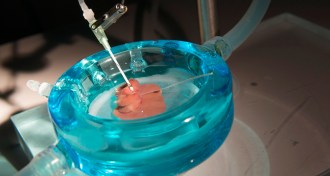
Health & MedicineSupercooling makes livers for transplants last longer
Supercooling a rat liver for transplant greatly increased an organ’s survival time outside the body, potentially opening the door for global allocation of human organs.
By Nsikan Akpan -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineCandidate asthma and allergy drug passes early test
By suppressing an inflammation-causing antibody, an experimental drug can lessen allergy and asthma symptoms for months at a time.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceAutism may carry a benefit: a buffer against Alzheimer’s
Brain plasticity of people with autism may protect them from Alzheimer’s disease, scientists propose.
-
 Life
LifeTibetans live high life thanks to extinct human relatives
DNA shared by modern-day Tibetans and extinct Denisovans suggests people picked up helpful genes through interbreeding with other hominids.