Humans
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Anthropology
Anthropology‘Hobbit’ may have been human with Down syndrome
A reanalysis of a skull scientists used to argue for the hobbit species Homo floresiensis suggests the woman was a modern human with features of Down syndrome.
-
 Health & Medicine
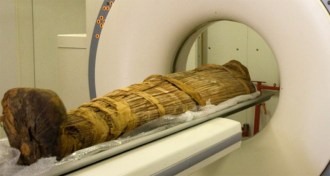
Health & MedicineMummies reveal hardened arteries
Mummy studies suggest heart disease is an ancient malady, not just the product of modern diets and sedentary lifestyles.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineSeven facts and a mystery about hand, foot and mouth disease
Hand, foot and mouth disease is a viral illness that most kids get before age 5. Several different viruses cause the condition, which causes blisters and fevers.
-
 Neuroscience
NeurosciencePart of brain’s pleasure network curbed in mice with chronic pain
Part of brain’s pleasure network is muffled in mice with chronic paw injuries, a new study finds.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineFist bumps spread fewer bacteria than handshakes
Fist bumping spreads far fewer bacteria than a handshake or a high five, a new study shows.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineResistance to key malaria drug spreads
Parasites that are less susceptible to artemisinin now affect several Asian countries.
By Nathan Seppa -
 Psychology
PsychologyGoalkeepers deceive themselves when facing penalty kicks
Soccer’s goalies fall victim to a logical fallacy during the sport’s most high-pressure situation, seeing trends where none exists.
By Nsikan Akpan -
 Health & Medicine
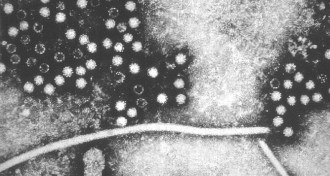
Health & MedicineHepatitis E widespread among English blood donors
Screening of 225,000 blood donations reveals a high prevalence of the hepatitis E virus.
-
 Tech
TechSmall lies in social networks may keep society running
Lying in social networks could have adverse, as well as beneficial, effects depending on the severity of the deception.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineBoot camp bug
Adenoviruses, which cause respiratory illnesses including some colds, plague boot camps.
By Nsikan Akpan -
 Genetics
GeneticsGene activity change can produce cancer
Scientists have long thought that epigenetic changes, which alter gene activity, can cause cancer. Now they have demonstrated it in a mouse experiment.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineLong-term Parkinson’s treatment sheds bad rep
Prolonged used of levodopa doesn’t increase the severity of side effects from the Parkinson’s drug, new research shows.