Humans
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
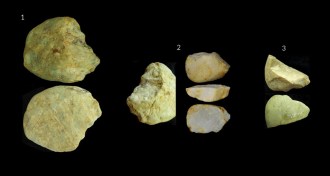 Archaeology
ArchaeologyMore signs emerge of New World settlers before 20,000 years ago
Controversial stone tools of pre-Clovis humans have been excavated in South America.
By Bruce Bower -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineTwo-part vaccine protects monkeys from Ebola
An experimental vaccine protected macaques from infection with the Ebola virus up to 10 months after receiving the two-shot regimen.
By Nathan Seppa -
 Genetics
GeneticsMolecular biologist honors ancient bones
After deciphering an ancient skeleton’s genetic secrets, molecular biologist Sarah Anzick helped reinter the remains.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineTest Ebola treatments to be rushed to West Africa
The World Health Organization has announced that it will use test treatments in West Africa starting this fall.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsA story about why people get fat may be just that
In this issue, reporters look at efforts to find the genes that could be responsible for the obesity crisis and how evolution acts on diseases such as Ebola and tuberculosis.
By Eva Emerson -

-
 Psychology
PsychologySimple rules can ease complex financial decisions
Straightforward strategies, known as heuristics, can be indispensable tools for keeping credit card debt in check as well as for making complex business decisions.
By Bruce Bower -
 Genetics
GeneticsAncient famine-fighting genes can’t explain obesity
Scientists question the long-standing notion that adaptation — specifically the evolution of genes that encourage humans to hold on to fat so they can survive times of famine — has driven the obesity crisis.
By Laura Beil -
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceChildren’s brains shaped by music training
After two years of an enrichment program, children’s brains showed more sophisticated response to spoken syllables.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineTrial drug improves heart failure patients’ chance of survival
Novartis’ experimental therapy LCZ696 lowers blood pressure and increases survival rates when compared with a standard drug.
By Nathan Seppa -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineA hungry brain slurps up a kid’s energy
Compared with other animals, human children take their time growing up. A new study suggests that’s because kids’ brains burn a lot of energy, perhaps diverting resources from their growing bodies.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineRemoving both breasts may not boost cancer survival
Women diagnosed with cancer in one breast who choose to have both breasts removed may not have better survival rates than women who opt for breast-conserving surgery and radiation.