Humans
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Science & Society
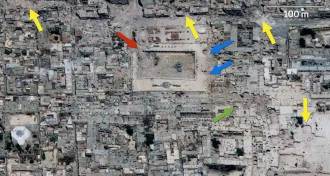
Science & SocietySyria’s World Heritage Sites severely damaged by war
Satellite images reveal that five of the country’s six World Heritage Sites have suffered damage and some structures have been completely destroyed.
By Beth Mole -
 Psychology
PsychologyBalancing the excitation and inhibition tightrope in depression
A new study looks at how a balance of positive and negative inputs in the lateral habenula might relate to disappointment and depression.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineRecovery time from surgery foretold
Blood samples taken from patients after surgery might reveal who is destined for a quick rebound.
By Nathan Seppa -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineThe debate over spanking is short on science, high on emotion
Spanking to discipline a child sparks heated debate that reflects deep divides in our society. Studies generally show negative effects of spanking, but there are many caveats.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineMore than 1 million Ebola cases may hit West Africa by January
New projections of the outbreak suggest that without drastic improvements, weekly cases could increase from hundreds to thousands.
By Nathan Seppa and Janet Raloff -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineGrowth in diabetes diagnoses starting to slow in U.S.
The percentage of the population diagnosed with diabetes and the rate of new cases per year rose sharply between 1990 and 2008 but haven't grown quite as quickly between 2008 and 2012.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineStatins may improve odds of surviving a bleeding stroke
Common cholesterol-lowering drugs called statins may help people who have suffered a stroke caused by ruptured blood vessels.
By Nathan Seppa -
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceDyslexic brain may solve some math problems in a roundabout way
Children with dyslexia rely heavily on right brain to do addition problems.
-
 Science & Society
Science & Society‘Fantastic Lab’ recounts battle against typhus, Nazis
Arthur Allen explores how two European scientists produced typhus vaccines during World War II.
-
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceFeedback
Readers discuss sources of stress in everyday life and tell us what they think about NASA's plan to nab an asteroid.
-
 Life
LifeThoughtful approach to antibiotic resistance
Changing how people think about antibiotics is already showing promise in reducing antibiotic use and costs. It’s doubtful, however, that any single strategy will be enough.
By Eva Emerson -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineDoctors enlisted to turn the tide on antibiotic resistance
Antibiotic stewardship requires education, diligence, and changes in prescribing. At some hospitals, it’s beginning to halt a dangerous trend.
By Nathan Seppa