Humans
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Genetics
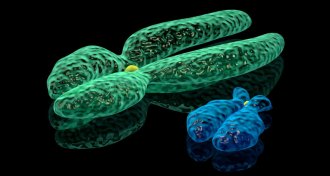
GeneticsMen who lose Y chromosome have high risk of cancer
Losing the Y chromosome in blood cells may bring on cancer and shorten men’s lives.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsEaster Islanders sailed to Americas, DNA suggests
Genetic ties among present-day populations point to sea crossings centuries before European contact with Easter Island.
By Bruce Bower -
 Humans
HumansOldest human DNA narrows time of Neandertal hookups
A 45,000-year-old Siberian bone provides genetic clues about the timing of interbreeding between ancient humans and Neandertals.
By Bruce Bower -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineThere’s no need to panic about enterovirus
The enterovirus behind this year’s outbreak, EV-D68, has been around for decades and generally causes mild symptoms.
-
 Humans
HumansAnglo-Saxons left language, but maybe not genes to modern Britons
Modern Britons may be more closely related to Britain’s indigenous people than they are to the Anglo-Saxons, a new genetic analysis finds.
-
 Psychology
PsychologyMajority doesn’t always rule in teen booze use
Having one abstainer as a friend cuts teens’ odds of getting drunk and binge drinking, a study finds.
By Bruce Bower -
 Health & Medicine
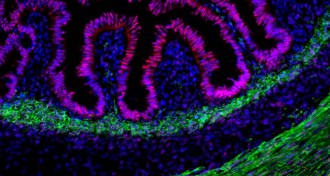
Health & MedicineTiny human intestine grown inside mouse
Human gut tissue transplanted into a mouse can grow into a working intestine that doctors could use to test disease treatments.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineFeedback
Readers discuss methods to prevent sepsis and whether genes are thrifty, while Tina Saey clears up some confusion regarding Ebola's airborne status.
-
 Microbes
MicrobesMicrobes can redeem themselves to fight disease
With some genetic engineering, bacteria can morph from bad to good and help attack invading cancer cells.
By Susan Gaidos -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicinePoop-transplant pills treat intestinal infection
Frozen capsules stuffed with healthy gut bacteria from donated poop fight C. difficile infections.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineJet lag affects gut microbes
Jet-lagged bacteria in the gut impair mice’s metabolism, causing obesity and diabetes-related problems.
-
 Health & Medicine
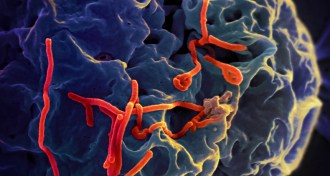
Health & MedicineEbola continues rapid spread in West Africa
Ebola continues to spread in West Africa, but some countries are poised to declare victory over the deadly virus.