Humans
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Chemistry
ChemistryChemist tackles complex problems with simplicity
Harvard chemist George Whitesides applies his unique problem-solving philosophy to creating new diagnostic devices for the developing world.
By Sam Lemonick -
 Psychology
PsychologyRip-off victims prefer compensation to retribution
But those acting on behalf of victims favor a punishment that fits the crime.
By Bruce Bower -
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceA species of invention
From early humans painting on cave walls to modern-day engineers devising ways to help people move better, the drive to innovate is simply part of who humans are.
By Eva Emerson -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineMini stomachs grown in lab
Clumps of human gastric cells could help researchers study stomach diseases.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHeavy milk drinking may double women’s mortality rates
In a study of 60,000 Swedes, drinking three or more classes of milk a day was associated with higher chances of death, cancer and hip fractures.
By Nathan Seppa -
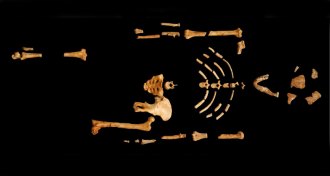 Humans
HumansHuman ancestor Lucy celebrates 40th anniversary
Paleoanthropologist Donald Johanson recalls the discovery 40 years ago of the human ancestor known as Lucy.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHarmless bacterium edges out intestinal germ
Researchers treated C. difficile infections in mice with a closely related bacteria that blocks C. difficile growth.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineDaylight savings time tied to more exercise in children
Kids in Europe and Australia are slightly more active in longer-lit evenings, a new study shows.
By Nathan Seppa -
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyIce Age hunter-gatherers lived at extreme altitudes
Two archaeological sites in the Andes indicate that hunter-gatherers inhabited extreme altitudes earlier than previously thought.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineCocoa antioxidants boost the aging brain
High doses of cocoa flavanols can improve some types of brain function in older individuals, a new study shows.
-
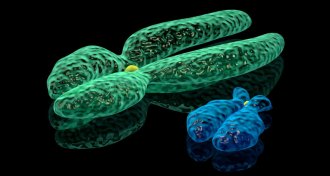 Genetics
GeneticsMen who lose Y chromosome have high risk of cancer
Losing the Y chromosome in blood cells may bring on cancer and shorten men’s lives.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsEaster Islanders sailed to Americas, DNA suggests
Genetic ties among present-day populations point to sea crossings centuries before European contact with Easter Island.
By Bruce Bower