Humans
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Artificial Intelligence
Artificial IntelligenceAre AI chatbot ‘personalities’ in the eye of the beholder?
Defining AI chatbot personality could be based on how a bot “feels” about itself or on how a person feels about the bot they’re interacting with.
By Sujata Gupta -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineToxic dangers lurk in LA, even in homes that didn’t burn
Urban wildfires like LA’s make harmful chemicals from burning plastics and electronics that can make indoor air dangerous for months.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicinePlastic shards permeate human brains
A study of microplastics and nanoplastics in brains shows an astonishing increase over time.
-
 Health & Medicine
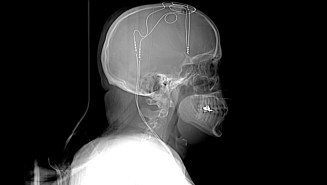
Health & MedicineWelcome to The Deep End, a new podcast about brain implants and depression
This new six-part podcast follows the lives of people with severe depression who volunteered for deep brain stimulation.
-
 Anthropology
AnthropologyAn African strontium map sheds light on the origins of enslaved people
While genetic tests can reveal the ancestry of enslaved individuals, strontium analysis can now home in on where they actually grew up.
-
 Health & Medicine
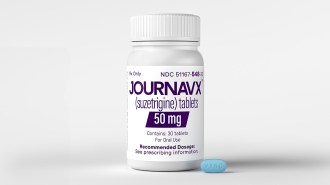
Health & MedicineA new kind of non-opioid painkiller gets FDA approval
The new drug, called Journavx, is a non-opioid for treating short-term moderate to severe pain.
-
 Neuroscience
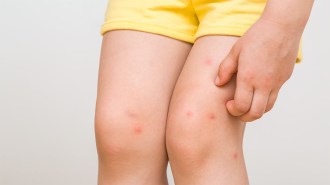
NeuroscienceScratching an itch is so good, and so bad
The motion kicks off inflammation but may also combat harmful bacteria
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineBetter male birth control is on the horizon
Men have two birth control options: condoms and vasectomies. Why has it taken so long to develop more contraceptives?
-
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyHere’s how ancient Amazonians became master maize farmers
Casarabe people grew the nutritious crop year-round on savannas thanks to networks of drainage canals and ponds.
By Bruce Bower -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineCan you actually die of a broken heart?
Death by heartbreak doesn't just happen in stories. In real life, severe stress can cause the sometimes-fatal takotsubo syndrome.
-
 Animals
AnimalsFever’s link with a key kind of immunity is surprisingly ancient
When sick, Nile tilapia seek warmer water. That behavioral fever triggers a specialized immune response, hinting the connection evolved long ago.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineTrump is withdrawing the U.S. from WHO. Here’s what that means
When Trump’s move to leave WHO takes effect in a year, it may gut funding for global public health and limit U.S. access to crucial data, experts warn.
By Meghan Rosen