Humans
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Tech
TechFacebook detects signs of postpartum depression
An analysis of Facebook activity can identify new moms with postpartum depression.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsEbola virus evolution tracked by genetic data
Analysis of Ebola genomes shows how the virus has evolved and some of the mutations that may thwart treatments.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineE-cigarettes may be gateway to addiction for teens
Teenagers are using e-cigarettes more than any other tobacco product and for many, it’s the first time they’ve tried a tobacco product at all.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineStoplights are hot spots for airborne pollution
Drivers get a big chunk of their exposure to pollutants from short stops at traffic intersections.
-
 Animals
AnimalsWhen you’re happy and you show it, dogs know it
A new test using pictures of halves of human faces challenges dogs’ abilities to read people’s emotions.
By Susan Milius -
 Genetics
GeneticsAncient East Asians mixed and mingled multiple times with Neandertals
East Asians’ ancestors interbred with Neandertals more than once, explaining why modern East Asians carry more Neandertal DNA than Europeans do, two studies suggest.
-
 Psychology
PsychologyScientists of a feather flock together
When it comes to major scientific issues such as global warming and GMOs, scientists and the public don’t see eye to eye. It might be because socially, they don’t see each other at all.
-
 Health & Medicine
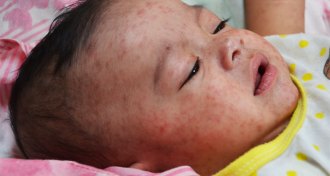
Health & MedicineU.S. measles tally for 2015 now at 121 cases
The 2014–2015 measles outbreak in the United States has now reached people in 17 states and the District of Columbia.
By Nathan Seppa -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineGlowing amino acid lights up growing brain cancer
By adding a tracer compound that sticks to the amino acid glutamine, researchers may be able to discern and monitor cancerous tissues in the brain.
By Nathan Seppa -
 Psychology
PsychologyAdults with autism are left to navigate a jarring world
Researchers are beginning to study ways to help adults with autism navigate independently, get jobs and find friendship.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineBouncing back from giving blood can take months
Taking iron supplements after donating blood can dramatically reduce the time it takes to recover iron levels in the blood, a study finds.
By Nathan Seppa -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineFallout from nuclear bomb testing presaged today’s radioactive tracers
Scientists in 1965 measured buildup of radioactive carbon from nuclear bomb testing in people.