Humans
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Humans
HumansNatural selection may be growing taller Dutch people
Over the past 200 years, natural selection may have driven the evolution of taller Dutch people, researchers posit.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineMutation regions mapped on genes that cause breast and ovarian cancer
An analysis of mutated BRCA genes could someday be used for personalized medicine in the fight against breast and ovarian cancer.
By Nathan Seppa -
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceBrains may be wired to count calories, make healthy choices
Fruit flies appear to make memories of the calories in the food they eat, an observation that may have implications for weight control in humans.
-
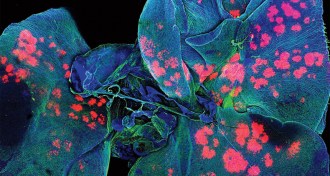 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicinePink blobs of hope in cancer-targeting quest
Cancer drugs coated with plastic can reach a mouse’s lungs for targeted delivery, but steering the capsules to the right spots can be a challenge.
-
 Anthropology
AnthropologyAncient Homo fossils found in Kenya
Finds from three individuals add to skeletal diversity of early members of human genus.
By Bruce Bower -
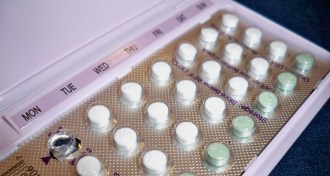 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineEarly birth control study probed effectiveness of pill
A 1960s study probed birth control pills’ effectiveness for women. Researchers are still trying to make a pill for men.
-
 Anthropology
AnthropologyFootprints offer clues about daily hominid life
Early male members of the human genus spent a lot of time together by the water, as their footprints attest.
By Bruce Bower -
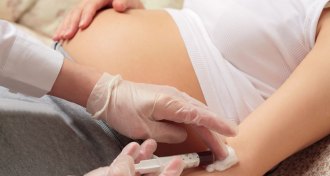 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineA more accurate prenatal test to predict Down syndrome
A test to detect genetic problems such as Down syndrome examines a baby’s DNA in the mother’s blood and may limit the need for more invasive screening.
-
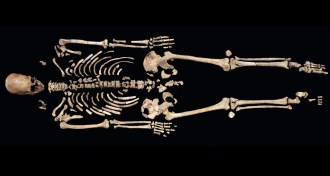 Anthropology
AnthropologyKennewick Man’s bones reveal his diet
Pacific Northwest man who lived 9,000 years ago ate from an almost entirely seafood menu, a new analysis finds.
By Bruce Bower -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineInjured baby hearts may be coaxed to regenerate
Shots of a growth factor protein reduce cell death in infant mice with heart damage.
By Nathan Seppa -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineOlder moms may have options to reduce newborns’ risks
Although babies born to older mothers face a higher danger of congenital heart defects, exercising moms may offset this added risk, a study in mice shows.
By Nathan Seppa -
 Tech
TechExoskeleton boot makes for more efficient walking
Newly developed exoskeleton boots that are unpowered are showing scientists that it is still possible to make walking even more efficient for humans.