Humans
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicinePerformance gains from Tommy John surgery still up for debate
Major league baseball pitchers who undergo two Tommy John surgeries have shorter careers than peers who don’t have the surgery, a new study finds.
By Nathan Seppa -
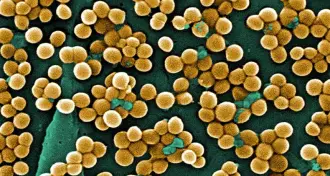 Science & Society
Science & SocietyWhite House unveils strategy against antibiotic resistance
The Obama Administration has launched a long-term plan to curb antibiotic resistance, unveiling incentives and requirements designed to boost surveillance and diagnosis of resistant microbes.
By Nathan Seppa -
 Psychology
PsychologyLong-term study complicates understanding of child abuse
Sexual abuse and neglect get reported more if parents were maltreated as kids, which may lead authorities to overestimate some children’s risk of abuse.
By Bruce Bower -
 Genetics
GeneticsIceland lays bare its genomes
A detailed genetic portrait of the Icelandic population is helping scientists to identify the genetic underpinnings of disease.
-
 Psychology
PsychologyRethinking light’s speed, helping young adults with autism and more reader feedback
Readers discuss the best ways to replicate findings in scientific studies, help teenagers with autism transition to adulthood, and more.
-
 Chemistry
ChemistryAir pollution molecules make key immune protein go haywire
Reactive molecules in air pollution derail immune responses in the lung and can trigger life-long asthma.
By Beth Mole -
 Astronomy
AstronomyWhat’s in a name? In science, a lot
Classification systems are essential to science. But any classification system, however useful, is ultimately simplistic.
By Eva Emerson -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineClean-up gene gone awry can cause Lou Gehrig’s disease
Scientists have linked mutations on a gene involved in inflammation and cell cleanup to ALS, or Lou Gehrig’s disease.
-
 Chemistry
ChemistryToday’s pot is more potent, less therapeutic
The medicinal qualities of marijuana may be up in smoke thanks to years of cross-breeding plants for a better buzz.
By Beth Mole -
 Anthropology
AnthropologyHow to reconstruct the face of an extinct human ancestor
3-D designer reconstructs portraits of ancestors for the human family album.
By Erin Wayman -
 Humans
HumansThe expressive face of human history on display
Busts on display in an Italian exhibit flesh out hominid skulls using the latest in 3-D reconstruction.
By Sean Treacy -
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyTelling stories from stone tools
Existing stone tool categories may hide more than they reveal. New methods for analyzing stone artifacts aim to better reconstruct how hominids interacted and moved across Africa, Asia and Europe.
By Bruce Bower