Humans
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineScience may get sidelined in artificial turf debate
Despite news reports about the potential harms of artificial turf, studies find synthetic fields have few health risks, although lead levels may be elevated in older fields.
By Beth Mole -
 Psychology
PsychologyBig ears don’t necessarily come with baggage
In a small study, adults judged children and teens with big ears as intelligent and likable.
-
 Climate
ClimateThe greatest natural disaster that almost was
The public’s response to the widest tornado ever recorded suggests earlier warnings need to be done right.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceBeing watched can boost productivity
In the company of another, a monkey steps up production on a simple job.
-
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyUnbiased computer confirms media bias
A computer algorithm can identify a media outlet’s bias just by the quotes it chooses from political speeches, surrounding context aside.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineApple’s ResearchKit wants your health data
Apple seeks recruits for health studies. But with uncertain measurements and lots of effort required to participate, the desire to help research may extend only so far.
-
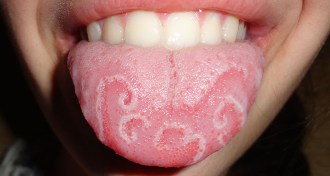 Life
Life‘Geographic tongue’ creates unique topography
A condition called ‘geographic tongue’ makes mouth organ appear maplike.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineSame mutations can show up in tumors, healthy tissues
Analyzing samples of healthy and tumor tissues could pinpoint which mutations are driving cancer and help develop better-targeted treatments.
By Nathan Seppa -
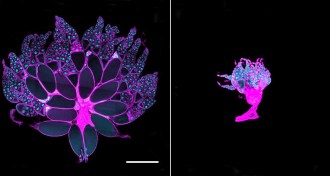 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineWhy cancer patients waste away
A tumor-produced protein that interferes with insulin causes wasting in fruit flies with cancer.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceNicotine exposure escalates rats’ desire for alcohol
Rats drink more alcohol after they’ve been hooked on nicotine.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineGenes may influence placebo effect
Certain gene variants may predispose people to experience the placebo effect, which may have implications for clinical trials and personalized medicine.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceMarijuana component fights epilepsy
A buzz-free extract of marijuana could help epilepsy patients whose seizures resist other treatments.
By Nathan Seppa