Humans
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Health & Medicine
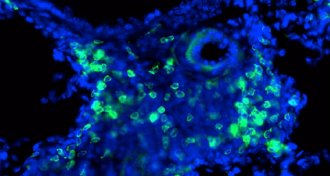
Health & MedicineSwitching off nerve cells eases asthma attacks
A drug that numbs nerve cells in mice’s airways offers a new way to ease the effects of an asthma attack.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Health & Medicine
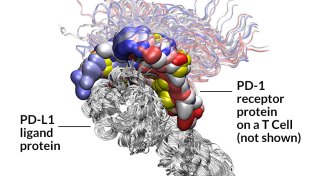
Health & MedicineNew cancer drugs wake up sleeping killer T cells
The immune system’s T cells, often evaded by tumors, might now resume the attack.
By Nathan Seppa -
 Psychology
PsychologyThe guilty pleasure of funny cat videos
Many people love posting and looking at cute kitty content online. A new survey shows that this could be because it helps us manage our emotions.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineSpit test could provide early warning of head, neck cancers
A new study shows that signs of head and neck cancer can be detected in saliva and blood plasma even before tumors are clinically diagnosed.
-
 Animals
AnimalsWhen baboons travel, majority rules
GPS study suggests baboons use simple rules to resolve travel disputes without leaders.
By Bruce Bower -
 Anthropology
AnthropologyKennewick Man’s DNA links him to present-day Native Americans
Genetic analysis of Kennewick Man suggests that the ancient Pacific Northwest man was most closely related to modern Native Americans, not Polynesians.
By Bruce Bower -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineCurtailing calories on a schedule yields health benefits
Eating an extreme low-calorie diet that mimics fasting just a few consecutive days a month may yield a bounty of health benefits, research suggests.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineAntibiotics can treat appendicitis
Antibiotics can successfully treat the majority of cases of a type of appendicitis, researchers find.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineRehab for psychopaths
Psychopaths often don’t fit movie stereotypes, but they share particular characteristics. New research shows that, contrary to popular thought, cognitive behavioral therapy can help some psychopaths stay out of prison.
By Bruce Bower -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineAntibiotics an alternative to surgery for appendicitis
Doctors could abandon routine surgery for uncomplicated cases of appendicitis, a new study suggests.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Genetics
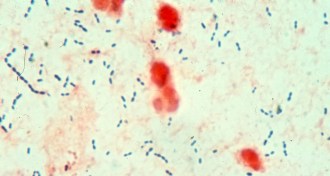
GeneticsPneumonia bacteria attacks lungs with toxic weaponry
Some strains of the bacteria that causes pneumonia splash lung cells with hydrogen peroxide to mess with DNA and kill cells, a new study suggests.
-
 Life
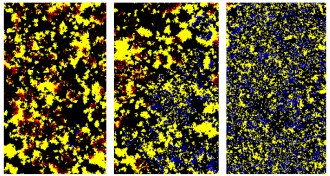
LifeAging: Nature’s way of reducing competition for resources
Aging may have developed in many species as a genetic mechanism to conserve future resources. If the controversial proposal is true, then scientists may be able to greatly extend life span by deactivating the machinery for aging embedded in our DNA.
By Andrew Grant