Humans
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Health & Medicine
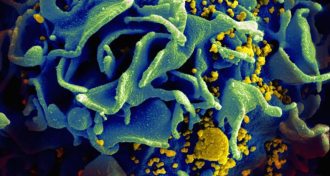
Health & MedicineEarlier is better for HIV treatment
People infected with HIV benefit from starting a drug regimen early, an international study finds.
By Nathan Seppa -
 Humans
HumansMoon bounces, bad spider leaders and more reader feedback
Readers debate faith's role in evolution, compare politicians to spiders and more.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineBlood test can predict breast cancer relapse
Blood tests for breast cancer DNA can predict relapse.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineVirus closely related to hepatitis A discovered in seals
Scientists have discovered a relative of the hepatitis A virus in seals.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceAltered protein makes mice smarter
By tweaking a single gene, scientists have turned average mice into supersmart daredevils.
-
 Anthropology
AnthropologyChilean desert cemetery tells tale of ancient trade specialists
Burial site holds clues to ancient trade brokers in Chilean desert.
By Bruce Bower -
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyA bot, not a Kardashian, probably wrote that e-cig tweet
Some 80 percent of recent e-cigarette-related tweets were promotional in nature, raising concerns that the positive spin is targeting a young audience.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceWhistled language uses both sides of the brain
Unlike spoken words, language made of whistles processed by both sides of the brain.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineFive reasons to not totally panic about ticks and Lyme disease
We’ve been trained to panic about tick bites and Lyme disease. There are risks to both — and here are some key facts.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineRecent advances may improve Jimmy Carter’s chances against melanoma
Improvements in melanoma treatment over the last five years may aid former President Jimmy Carter’s battle against the disease.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsGene thought to cause obesity works indirectly
Researchers have discovered a “genetic switch” that determines whether people will burn extra calories or save them as fat.
-
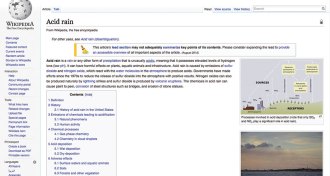 Science & Society
Science & SocietyContentious science topics on Wikipedia subject to editing mischief
Global warming and other politically charged issues are prime targets for sabotage on Wikipedia.
By Meghan Rosen