Humans
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineFor kids learning new words, it’s all about context
By recording the first three years of life, researchers get hints about a child’s language development.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineStudy finds benefits from lowering blood pressure, but questions remain
Preliminary results from NIH clinical trial suggest that lower blood pressure is better, but scientists have not yet published the data and open questions remain.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineCoffee reveals itself as an unlikely elixir
Coffee is earning a reputation as a health tonic, reducing risk for a long list of ailments and even lowering death rates.
By Nathan Seppa -
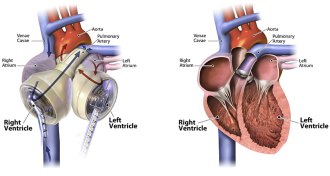 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineIn 1965, hopes were high for artificial hearts
Developing artificial hearts took longer than expected, and improved devices are still under investigation.
-

-
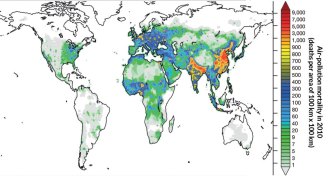 Environment
EnvironmentHome fires, farm fumes are leading causes of air-pollution deaths
Deadly air pollution comes from surprising sources, but toxicity of different types is still up in the air.
By Beth Mole -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineBackwash from nursing babies may trigger infection fighters
A nursing baby’s saliva may get slurped back into mom’s breast, where it stimulates an immune response.
-
 Psychology
PsychologyPeople find the skin of others’ softer than their own
Humans perceive other peoples’ skin as softer and smoother than their own because touch is important in social bonding, researchers suggest.
-
 Archaeology
Archaeology‘Superhenge’ once lined Stonehenge neighborhood
A row of massive, now-buried stones once bordered a site near Stonehenge.
By Bruce Bower -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineClinical trial suggests new blood pressure standard
Preliminary results from a clinical trial suggest lower blood pressure targets could reduce rates of cardiovascular diseasae.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicinePlant spills crucial details for making cancer drug
By injuring the Himalayan mayapple, researchers worked out how the plant makes an important ingredient in a common cancer drug.
By Beth Mole -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineLess vitamin D and melatonin bad for multiple sclerosis
Vitamin D and melatonin play important roles in multiple sclerosis.