Humans
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Archaeology
ArchaeologySearch for fossils from the comfort of home
The citizen science website FossilFinder.org lets anyone with an Internet connection look for fossils and characterize rocks at Kenya’s Lake Turkana Basin
By Erin Wayman -
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyMystery still surrounds Neandertals
Neandertals’ relationship to modern humans is still a matter of debate.
-
 Microbes
MicrobesGut microbes signal when dinner is done
Helpful E. coli bacteria that live in the guts of animals produce proteins that can decrease an animal’s appetite only 20 minutes after receiving nutrients
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHaving parasites can boost fertility
Infection with parasitic worms tinkers with fertility.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Health & Medicine
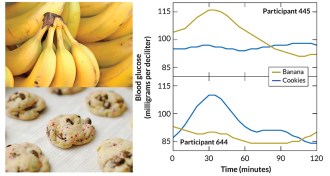
Health & MedicineA good diet for you may be bad for me
Eating the same foods can produce very different reactions in people.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineEngineered vocal cords show promise in animal tests
Lab-grown vocal cord tissue could lead the way to better treatments for people with vocal problems
-
 Psychology
PsychologyCulture shapes sense of fairness
Culture shapes kids’ sense of fairness, especially when they get the short end of the stick.
By Bruce Bower -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineWhen selenium is scarce, brain battles testes for it
In competition for selenium, testes draw the nutrient away from the brain.
-
 Psychology
PsychologyCaffeine gives cocaine an addictive boost
Not only is it popular to “cut” cocaine with caffeine, the combination might be more addictive.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineStudy brews up more evidence for coffee’s health benefits
Drinking up to five cups of coffee a day reduced the risk of dying early from heart and brain diseases and suicide.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineStudy brews up more evidence for coffee’s health benefits
Drinking up to five cups of coffee a day reduced the risk of dying early from heart and brain diseases and suicide.
-
 Anthropology
AnthropologyDNA puts Neandertal relatives in Siberia for 60,000 years
Recovered DNA suggests Denisovans inhabited Siberia for around 60,000 years.
By Bruce Bower