Humans
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceRe-creating womb sounds perks preemies’ attention
Babies born prematurely may benefit from hearing a recording of their mothers’ voices and heartbeats.
-
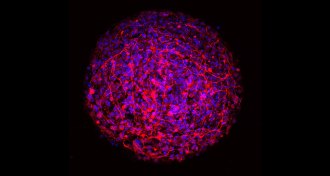 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceTiny bare-bones brains made in lab dishes
A reliable way to make standard-issue minibrains could help scientists study the human brain.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceEarly exposure to signing helps deaf kids on mental task
Deaf kids exposed to sign language from birth performed better on a task that required attention and impulse control.
-
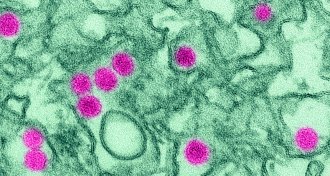 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineUnknowns about Zika virus continue to frustrate
As worry about the Zika virus outbreak continues to ratchet up, scientists are scrambling to understand what threats the virus poses and how to stop it from spreading.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Environment
EnvironmentVaping linked to host of new health risks
Animal studies and analyses of gene activity point to broad range of potential new health risks from vaping affecting everything from sperm to heart and immunity to mental health.
By Janet Raloff -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineThe best advice on Zika virus and pregnancy is to know the unknowns
There are some practical steps pregnant women and women who want to be pregnant can take to minimize risk of Zika virus infection.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsNeandertal DNA may raise risk for some modern human diseases
Neandertal DNA may once have helped humans, but now may contribute to disease.
-
 Anthropology
AnthropologyRise of human civilization tied to belief in punitive gods
Beliefs in all-knowing, punitive deities may have fueled the growth of human civilizations.
By Bruce Bower -
 Animals
AnimalsAfrica’s poison arrow beetles are key in traditional hunting method
In the Kalahari of Namibia, some San people still hunt with a traditional method — arrows laced with poison taken from beetle larvae.
-
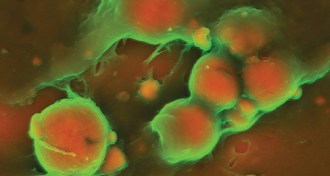 Life
LifeImages probe artery-hardening plaques
Zooming in on hardened arteries shows researchers which plaques pose heart attack risks.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceCancer drug’s usefulness against Alzheimer’s disputed
A preliminary report questions the anti-Alzheimer’s activity of a cancer-fighting drug.
-
 Psychology
PsychologyDon’t blame winter for that bleak mood
Contrary to popular opinion, depression doesn’t spike in winter, survey finds.
By Bruce Bower