Humans
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineMath offers new view of brain and its disorders
Editor in chief Eva Emerson discusses new insights into the brain's role in mental illness, sleep, and ancient rituals.
By Eva Emerson -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineZika, psychobiotics and more in reader feedback
Readers respond to the April 2, 2016, issue of Science News with thoughts on Zika virus, planetary science, microbes in mental health and more.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineWith easy e-cig access, teen vaping soars
The vast majority of U.S. states ban sales or distribution of e-cigarette products to minors. Still, it’s no sweat for teens to buy them online.
By Janet Raloff -
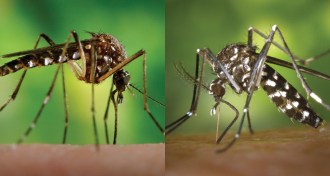 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineScientists wrestle with possibility of second Zika-spreading mosquito
It’s hard to say yet whether Asian tiger mosquitoes will worsen the ongoing Zika outbreak in the Americas.
By Susan Milius -
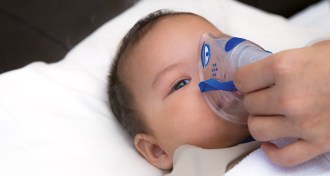 Genetics
GeneticsFaulty gene can turn colds deadly for babies, toddlers
Children with a faulty virus-sensing gene may land in intensive care after a cold.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHere are a few more things for the childproofing list
Some seemingly safe objects may be particularly dangerous for little kids.
-
 Anthropology
Anthropology‘Slam-dunk’ find puts hunter-gatherers in Florida 14,500 years ago
Finds at an underwater site put people in Florida a surprisingly long time ago.
By Bruce Bower -
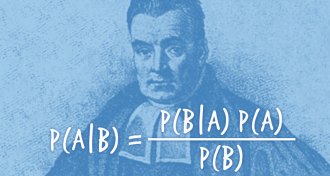 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceBayesian reasoning implicated in some mental disorders
An 18th century math theory may offer new ways to understand schizophrenia, autism, anxiety and depression.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceBrain waves in REM sleep help store memories
Mice with disturbed REM sleep show memory trouble.
-
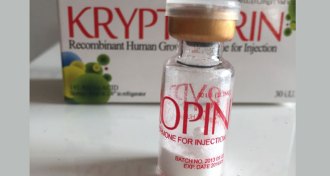 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineEarly work on human growth hormone paved way for synthetic versions
In 1966, researchers reported the complete chemical structure of human growth hormone. Today synthetic growth hormone is used to treat growth hormone deficiency.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHealthiest weight just might be ‘overweight’
The body mass index tied to lowest risk of death has risen since the 1970s. It now falls squarely in the “overweight” category.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineMouse studies link Zika virus infection to microcephaly
Three new studies in mice shore up the link between microcephaly and Zika virus infection.
By Meghan Rosen