Humans
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineRiding roller coasters might help dislodge kidney stones
Researchers took a 3-D printed kidney containing tiny stones and urine for a spin on a roller coaster and found their patients’ stories of kidney stones passing on the ride to have merit.
By Laura Beil -
 Psychology
PsychologyLearning curve not so smooth
Preschoolers tend to reach a milestone of social thinking after months of fits and starts.
By Bruce Bower -
 Paleontology
PaleontologyPicture of primate common ancestor coming into focus
A new family tree analysis predicts behavior of primate common ancestor.
By Erin Wayman -
 Genetics
GeneticsAncient hookups gave chimps a smidge of bonobo DNA
Genetic evidence suggests bonobos and chimpanzees interbred after becoming separate species.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineTraining for parents may lessen some autism symptoms in kids
Training parents may help with some autism symptoms, a new study suggests.
-
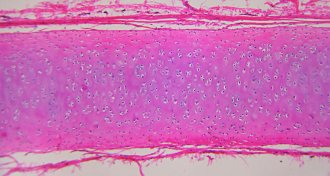 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineNose cells fix knee cartilage
A small clinical trial suggests that using nose cells to patch knee cartilage could be a viable treatment for injuries.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineNose cells fix knee cartilage in human trial
A small clinical trial suggests that using nose cells to patch knee cartilage could be a viable treatment for injuries.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineScreen time guidelines for kids give parents the controls
New recommendations for children’s media use are more nuanced than earlier guidelines, a change that reflects the shifting technology landscape.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsDNA data offer evidence of unknown extinct human relative
Melanesians may carry genetic evidence of a previously unknown extinct human relative.
-
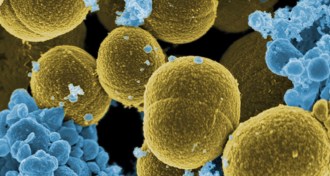 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineStaph infections still a concern
Scientists have been searching for a vaccine against a deadly microbe for 50 years.
-
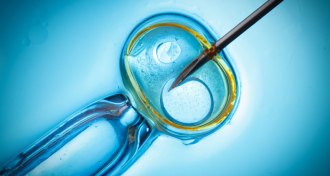 Health & Medicine
Health & Medicine‘Three-parent baby’ boy healthy so far
A baby boy born with donor mitochondrial DNA seems to be healthy, researchers report at a meeting.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsReaders question the biology of alcoholism and more
Alcoholism-linked genes, making better corneas and more in reader feedback.